Factors related to lithium blood concentrations in Chinese Han patients with bipolar disorder
- PMID: 31371966
- PMCID: PMC6628605
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S205780
Factors related to lithium blood concentrations in Chinese Han patients with bipolar disorder
Abstract
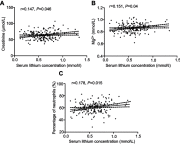
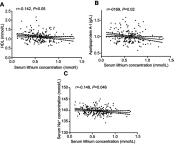
Background: The goal of this study was to identify the physiological factors related to the blood concentration of lithium in Chinese Han patients with bipolar disorder (BD). Materials and methods: A total of 186 Chinese Han patients with BD were assessed. Patients were recruited from the Anhui Mental Health Center. The concentrations of serum lithium were measured by a Dimension RxL Max biochemistry analyzer. Physiological factors, including body weight, body mass index (BMI), and routine laboratory parameters, were collected. Relationships between the serum lithium concentration and relevant clinical data were analyzed by Pearson correlation tests, and the independent relationships were determined by multivariate linear regression analysis. Results: Pearson correlation analysis showed that serum lithium concentrations were positively correlated with creatinine concentrations (r=0.147, P=0.046), Mg2+ concentrations (r=0.151, P=0.04), and the percentage of neutrophils (r=0.178, P=0.015) and negatively correlated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) concentrations (r=-0.142, P=0.05), apolipoprotein A1 concentrations (r=-0.169, P=0.02), and Na+ concentrations (r=-0.148, P=0.046) in 186 patients with BD. Furthermore, multivariate linear regression analysis showed that serum lithium concentrations were negatively associated with Na+ concentrations and positively associated with the percentage of neutrophils. Conclusion: These results suggest that physiological factors, including creatinine, HDL, apolipoprotein A1, Na+, and Mg2+ concentrations and percentage of neutrophils, might be related to serum lithium concentrations and provide a basis for parameter selection of lithium population pharmacokinetics in Chinese Han patients with BD.
Keywords: apolipoprotein A1; bipolar disorder; creatinine; high-density lipoprotein; lithium; neutrophil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prevalence and clinical-demographic correlates of hyperhomocysteinemia in inpatients with bipolar disorder in a Han Chinese population.Psychiatry Res. 2018 Jan;259:364-369. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.08.063. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Psychiatry Res. 2018. PMID: 29120844
-
Association between decreased HDL levels and cognitive deficits in patients with bipolar disorder: a pilot study.Int J Bipolar Disord. 2019 Nov 25;7(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40345-019-0159-7. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2019. PMID: 31761966 Free PMC article.
-
Safety monitoring of treatment in bipolar disorder in a tertiary care setting in Sri Lanka and recommendations for improved monitoring in resource limited settings.BMC Psychiatry. 2019 Jun 24;19(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12888-019-2183-7. BMC Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31234824 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium in Bipolar Disorder: Optimizing Therapy Using Prolonged-Release Formulations.Drugs R D. 2016 Dec;16(4):293-302. doi: 10.1007/s40268-016-0139-7. Drugs R D. 2016. PMID: 27770296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lithium in bipolar disorder: can drug concentrations predict therapeutic effect?Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(9):639-60. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200241090-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002. PMID: 12126457 Review.
Cited by
-
External Evaluation of Population Pharmacokinetics Models of Lithium in the Bipolar Population.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 18;16(11):1627. doi: 10.3390/ph16111627. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004492 Free PMC article.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Lithium in Young Pediatric Patients With Intellectual Disability.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 15;12:650298. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.650298. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33935755 Free PMC article.
-
Individualization of lithium therapy based on the monitoring of its level in saliva.Postep Psychiatr Neurol. 2021 Dec;30(4):251-257. doi: 10.5114/ppn.2021.111938. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Postep Psychiatr Neurol. 2021. PMID: 37082561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Candidates for Biomarkers in Bipolar Disorder: A Proteomic Approach through Systems Biology.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2022 May 31;20(2):211-227. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2022.20.2.211. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35466093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saliva testing as a means to monitor therapeutic lithium levels in patients with psychiatric disorders: Identification of clinical and environmental covariates, and their incorporation into a prediction model.Bipolar Disord. 2021 Nov;23(7):679-688. doi: 10.1111/bdi.13128. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Bipolar Disord. 2021. PMID: 34536974 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

