Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 31372019
- PMCID: PMC6628146
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S208989
Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Abstract
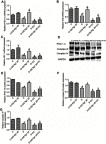
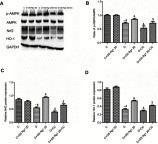
Background and purpose: Ginsenoside Rg1 (GS Rg1), as an important active substance of Panax ginseng, has been proven to have elaborate cardioprotective effects. The purpose of this study was to detect that GS Rg1 attenuates cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats (DM). Methods: Cardiac function was assessed by heart rate and blood pressure. Markers relevant to myocardial oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity, and inflammatory reaction factors were detected. The mRNA and protein expression were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot, respectively. Results: GS Rg1 treatment significantly reduced the symptoms of cardiac hypertrophy and hypertension, and also decreased oxidative stress, inflammation response, NF-κB expression and NLRP3 inflammasome expression. GS Rg1 enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis by increasing PGC-1α, complex III and complex Ⅳ expression. GS Rg1 treatment significantly increased the expression of AMPK, Nrf2 and HO-1 in cardiac tissues. Conclusion: GS Rg1 exhibited protective effect against STZ-induced cardiac dysfunction, which is potentially associated with AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway.
Keywords: AMPK; Ginsenoside Rg1; HO-1; Nrf; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
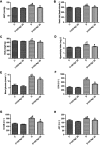
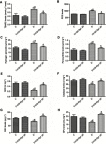
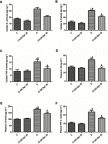
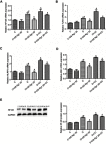
Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 protects mice against streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic by modulating the NLRP3 and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 5;866:172801. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172801. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31738935
-
Pterostilbene Decreases Cardiac Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via Activation of AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Fructose-Fed Diabetic Rats.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018 Apr;32(2):147-163. doi: 10.1007/s10557-018-6780-3. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018. PMID: 29556862
-
Cardioprotective Effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum against Streptozotocin Induced Cardiac Toxicity in Rats via Alteration of AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.J Oleo Sci. 2022;71(7):991-1002. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess21281. J Oleo Sci. 2022. PMID: 35781259
-
Protective Effects and Target Network Analysis of Ginsenoside Rg1 in Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury: A Comprehensive Overview of Experimental Studies.Cells. 2018 Dec 12;7(12):270. doi: 10.3390/cells7120270. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30545139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepataprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 - A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jul 12;206:178-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.04.012. Epub 2017 Apr 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28427912 Review.
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 can restore hematopoietic function by inhibiting Bax translocation-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis in aplastic anemia.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 17;11(1):12742. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91471-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34140535 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 exerts anti-arrhythmic effect by inhibiting ICaL through cAMP-PKA and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways in rat ventricular myocytes after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Sci Prog. 2025 Apr-Jun;108(2):368504251341113. doi: 10.1177/00368504251341113. Epub 2025 May 23. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40405681 Free PMC article.
-
Shenqi Lixin Decoction improves cardiac function in rats with adriamycin-induced heart failure through modulation of PGC-1α and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Oct;9(20):1592. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5350. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34790798 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Nrf2 signaling pathway in diabetic cardiomyopathy: from pathogenesis to traditional Chinese medicine interventions.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 14;12:1492499. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1492499. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40727576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes cardiomyopathy: targeted regulation of mitochondrial dysfunction and therapeutic potential of plant secondary metabolites.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 9;15:1401961. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1401961. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39045049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Dieren S, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, Grobbee DE, Nealb B. The global burden of diabetes and its complications: an emerging pandemic. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010;17(Suppl 1):S3–S8. - PubMed
-
- Boudina S, Abel ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. 2007;115(52):3213–3223. - PubMed
-
- Asrih M, Steffens S. Emerging role of epigenetics and miRNA in diabetic cardio- myopathy. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(2):117–125. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

