Impact of clinical features on the efficacy of osimertinib therapy in patients with T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer and acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 31372272
- PMCID: PMC6626778
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2019.06.03
Impact of clinical features on the efficacy of osimertinib therapy in patients with T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer and acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Osimertinib exhibits good efficacy in patients with T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Compared with the clinical trials, in real-world clinical practice, osimertinib must be administered to older patients and those with poor Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG-PS). Therefore, we investigated the association between osimertinib efficacy/safety and PS score, age, and other clinical features in patients with T790M-positive NSCLC.
Methods: We reviewed all patients with T790M-positive NSCLC and acquired resistance to initial EGFR-TKIs who were administered osimertinib between March 2016 and January 2018 at the Tokyo Metropolitan Cancer and Infectious Diseases Center in Komagome Hospital, Japan.
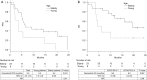
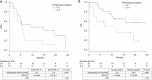
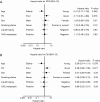
Results: In total, 31 patients, including 8 young (<65 years) and 23 elderly (≥65 years) patients, were included in the study. Of these, 10 (32.3%) patients had poor PS scores. The progression-free survival (PFS) was significantly shorter in young patients was than elderly patients [3.5 vs. 6.4 months, P=0.041; hazard ratio (HR), 2.41]. The overall survival (OS) of the young patients tended to be shorter than that of the elderly patients (5.3 vs. 19.4 months, P=0.067; HR, 2.58). The PFS (9.1 vs. 5.5 months; P=0.071; HR, 0.38) and the OS (not reached vs. 6.6 months, P=0.061; HR, 0.39) were shorter in patients with poor ECOG-PS than those with good ECOG-PS. The toxic effects of osimertinib were manageable. By multivariate analysis, both age and ECOG-PS were independent predictors of osimertinib efficacy.
Conclusions: Poor ECOG-PS and younger age were associated with lower efficacy of osimertinib in T790M-positive NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI; Lung cancer; Threonine790Methionine; epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); osimertinib.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Y Hosomi, Y Okuma, K Kubota, M Seike and A Gemma have received honoraria from AstraZeneca. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Comment in
-
Impact of performance status and age on osimertinib efficacy in patients with EGFR-mutant T790M-positive non-small-cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Sep;11(Suppl 15):S1831-S1834. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.08.104. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31632761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Relationship between performance status or younger age and osimertinib therapy in T790M-positive NSCLC: are the available data convincing?J Thorac Dis. 2019 Sep;11(Suppl 15):S1837-S1840. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.08.99. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31632763 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Respecting your elders: osimertinib demonstrates preferential activity in elderly patients with T790M positive non-small cell lung cancers.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Sep;11(Suppl 15):S1844-S1846. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.08.122. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31632765 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of clinical features on the efficacy of osimertinib treatment in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors due to T790M mutation.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Sep;11(Suppl 15):S1847-S1851. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.08.117. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31632766 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Does osimertinib treatment discriminate young patients?J Thorac Dis. 2019 Sep;11(Suppl 15):S1852-S1854. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.08.118. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31632767 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of clinical features of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients on osimertinib efficacy.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Nov;11(11):4400-4403. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.10.67. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31903227 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The impact of age and performance status on the efficacy of osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Mar;12(3):153-155. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.12.80. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32274079 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:239-46. 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2014;15:213-22. 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70604-1 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
