High-fidelity, high-isotropic-resolution diffusion imaging through gSlider acquisition with and T1 corrections and integrated ΔB0 /Rx shim array
- PMID: 31373048
- PMCID: PMC6778699
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27899
High-fidelity, high-isotropic-resolution diffusion imaging through gSlider acquisition with and T1 corrections and integrated ΔB0 /Rx shim array
Abstract
Purpose: and T1 corrections and dynamic multicoil shimming approaches were proposed to improve the fidelity of high-isotropic-resolution generalized slice-dithered enhanced resolution (gSlider) diffusion imaging.
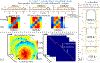
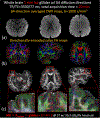
Methods: An extended reconstruction incorporating inhomogeneity and T1 recovery information was developed to mitigate slab-boundary artifacts in short-repetition time (TR) gSlider acquisitions. Slab-by-slab dynamic B0 shimming using a multicoil integrated ΔB0 /Rx shim array and high in-plane acceleration (Rinplane = 4) achieved with virtual-coil GRAPPA were also incorporated into a 1-mm isotropic resolution gSlider acquisition/reconstruction framework to achieve a significant reduction in geometric distortion compared to single-shot echo planar imaging (EPI).
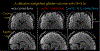
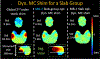
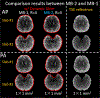
Results: The slab-boundary artifacts were alleviated by the proposed and T1 corrections compared to the standard gSlider reconstruction pipeline for short-TR acquisitions. Dynamic shimming provided >50% reduction in geometric distortion compared to conventional global second-order shimming. One-millimeter isotropic resolution diffusion data show that the typically problematic temporal and frontal lobes of the brain can be imaged with high geometric fidelity using dynamic shimming.
Conclusions: The proposed and T1 corrections and local-field control substantially improved the fidelity of high-isotropic-resolution diffusion imaging, with reduced slab-boundary artifacts and geometric distortion compared to conventional gSlider acquisition and reconstruction. This enabled high-fidelity whole-brain 1-mm isotropic diffusion imaging with 64 diffusion directions in 20 min using a 3T clinical scanner.
Keywords: inhomogeneity; diffusion-weighted imaging; gSlider; shim array.
© 2019 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures

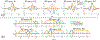

References
-
- Mansfield P Multi-planar image formation using NMR spin echoes. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys 1977;10:L55–L58 doi: 10.1088/0022-3719/10/3/004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 EB025162/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116173/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 EB021349/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019254/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019307/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB020613/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 EB026996/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U24 EB028984/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS096056/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB016695/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015896/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023401/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

