Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Croton hypoleucus Extract in an Induced-Necrosis Model in Rats
- PMID: 31373296
- PMCID: PMC6680924
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24142533
Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Croton hypoleucus Extract in an Induced-Necrosis Model in Rats
Abstract
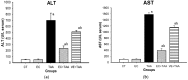
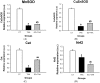
The aim of this study was to evaluate the antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Croton hypoleucus (EC). The present work reports the first pharmacological, toxicological, and antioxidant studies of EC extract on liver injury. Liver necrosis was induced by thioacetamide (TAA). Five groups were established: Croton Extract (EC), thioacetamide (TAA), Croton extract with thioacetamide (EC + TAA), vitamin E with thioacetamide (VE + TAA) and the positive control and vehicle (CT). For EC and EC + TAA, Wistar rats (n = 8) were intragastrically pre-administered for 4 days with EC (300 mg/kg.day) and on the last day, EC + TAA received a single dose of TAA (400 mg/kg). At 24 h after damage induction, animals were sacrificed. In vitro activity and gene expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (Cat), and Nrf2 nuclear factor were measured. The results show that EC has medium antioxidant properties, with an IC50 of 0.63 mg/mL and a ferric-reducing power of 279.8 µM/mg. Additionally, EC reduced hepatic damage markers at 24 h after TAA intoxication; also, it increased SOD and Cat gene expression against TAA by controlling antioxidant defense levels. Our findings demonstrated the hepatoprotective effect of EC by reducing hepatic damage markers and controlling antioxidant defense levels. Further studies are necessary to identify the mechanism of this protection.
Keywords: Croton hypoleucus; antioxidant activity; hepatoprotective effect; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) The World Medicines Situation, Traditional Medicines: Global Situation, Issues and Challenges. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011. 12p
-
- Salatino A., Salatino M.L.F., Negri G. Traditional uses, chemistry and pharmacology of Croton species (Euphorbiaceae) J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007;18:11–33. doi: 10.1590/S0103-50532007000100002. - DOI
-
- Adewusi E.A., Afolayan A.J. A review of natural products with hepatoprotective activity. JMPR. 2010;4:1318–1334. doi: 10.5891/JMPR09.472. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

