Possible magneto-mechanical and magneto-thermal mechanisms of ion channel activation in magnetogenetics
- PMID: 31373554
- PMCID: PMC6693891
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.45807
Possible magneto-mechanical and magneto-thermal mechanisms of ion channel activation in magnetogenetics
Abstract
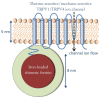
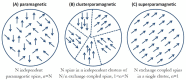
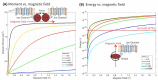
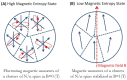
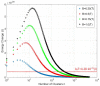
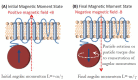
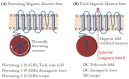
The palette of tools for perturbation of neural activity is continually expanding. On the forefront of this expansion is magnetogenetics, where ion channels are genetically engineered to be closely coupled to the iron-storage protein ferritin. Initial reports on magnetogenetics have sparked a vigorous debate on the plausibility of physical mechanisms of ion channel activation by means of external magnetic fields. The criticism leveled against magnetogenetics as being physically implausible is based on the specific assumptions about the magnetic spin configurations of iron in ferritin. I consider here a wider range of possible spin configurations of iron in ferritin and the consequences these might have in magnetogenetics. I propose several new magneto-mechanical and magneto-thermal mechanisms of ion channel activation that may clarify some of the mysteries that presently challenge our understanding of the reported biological experiments. Finally, I present some additional puzzles that will require further theoretical and experimental investigation.
Keywords: mouse; neuroscience; none; rat.
© 2019, Barbic.
Conflict of interest statement
MB No competing interests declared
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid Oxidation Induced by RF Waves and Mediated by Ferritin Iron Causes Activation of Ferritin-Tagged Ion Channels.Cell Rep. 2020 Mar 10;30(10):3250-3260.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.070. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32160534 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological Mechanisms and Validation of Ferritin-Based Magnetogenetics for Remote Control of Neurons.J Neurosci. 2024 Jul 24;44(30):e1717232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1717-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38777598 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering a Genetically Encoded Magnetic Protein Crystal.Nano Lett. 2019 Oct 9;19(10):6955-6963. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b02266. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Nano Lett. 2019. PMID: 31552740 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetogenetics: remote activation of cellular functions triggered by magnetic switches.Nanoscale. 2022 Feb 10;14(6):2091-2118. doi: 10.1039/d1nr06303k. Nanoscale. 2022. PMID: 35103278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetogenetics as a promising tool for controlling cellular signaling pathways.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jun 10;22(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02616-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38858689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bidirectional regulation of motor circuits using magnetogenetic gene therapy.Sci Adv. 2024 Oct 11;10(41):eadp9150. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp9150. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39383230 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanogenetics for cellular engineering and cancer immunotherapy.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;66:88-94. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2020.06.008. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32717634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering a possible role of reactive oxygen species in magnetogenetics.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 4;10(1):13096. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70067-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32753716 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Oxidation Induced by RF Waves and Mediated by Ferritin Iron Causes Activation of Ferritin-Tagged Ion Channels.Cell Rep. 2020 Mar 10;30(10):3250-3260.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.070. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32160534 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in magnetic nanoparticles for molecular medicine.Chem Commun (Camb). 2025 Feb 13;61(15):3093-3108. doi: 10.1039/d4cc05167j. Chem Commun (Camb). 2025. PMID: 39846549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arora SK, Wu H-C, Choudhary RJ, Shvets IV, Mryasov ON, Yao H, Ching WY. Giant magnetic moment in epitaxial fe(3)O(4) thin films on MgO(100) Physical Review. B, Condensed Matter. 2008;77:e134443. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.77.134443. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

