Blocking the histone lysine 79 methyltransferase DOT1L alleviates renal fibrosis through inhibition of renal fibroblast activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 31373855
- PMCID: PMC8793787
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201801861R
Blocking the histone lysine 79 methyltransferase DOT1L alleviates renal fibrosis through inhibition of renal fibroblast activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
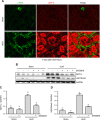
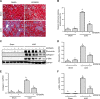
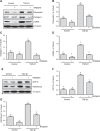
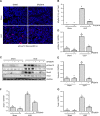
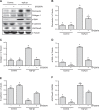
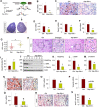
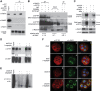
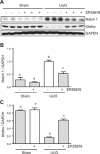
Disruptor of telomeric silencing-1 like (DOT1L) protein specifically catalyzes the methylation of histone H3 on Lys79 (H3K79) and is implicated in tumors. But its role in tissue fibrosis remains unclear. Here we demonstrated that injury to the kidney increased DOT1L expression and H3K79 dimethylation in renal tubular epithelial cells and myofibroblasts in a murine model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Administration of EPZ5676, a highly selective inhibitor of DOT1L, attenuated renal fibrosis. Treatment with EPZ5676 or DOT1L small interfering RNA also inhibited TGF-β1 and serum-induced activation of renal interstitial fibroblasts and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in vitro. Moreover, blocking DOT1L abrogated injury-induced epithelial G2/M arrest; reduced expression of Snail, Twist, and Notch1; and inactivated several profibrotic signaling molecules in the injured kidney, including Smad3, epidermal growth factor receptor, platelet-derived growth factor receptor, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, protein kinase B, and NF-κB. Conversely, DOT1L inhibition increased expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog, a protein associated with dephosphorylation of tyrosine kinase receptors, and prevented decline in levels of Klotho and Smad7, 2 renoprotective factors. Thus, our data indicate that targeting DOT1L attenuates renal fibrosis through inhibition of renal fibroblasts and EMT by suppressing activation of multiple profibrotic signaling pathways while retaining expression of renoprotective factors.-Liu, L., Zou, J., Guan, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Zhou, X., Xiong, C., Tolbert, E., Zhao, T. C., Bayliss, G., Zhuang, S. Blocking the histone lysine 79 methyltransferase DOT1L alleviates renal fibrosis through inhibition of renal fibroblast activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Keywords: ERSD; Notch1; Smad3; Snail; transforming growth factor.
Figures


References
-
- Zoccali, C. , Vanholder, R. , Massy, Z. A. , Ortiz, A. , Sarafidis, P. , Dekker, F. W. , Fliser, D. , Fouque, D. , Heine, G. H. , Jager, K. J. , Kanbay, M. , Mallamaci, F. , Parati, G. , Rossignol, P. , Wiecek, A. , and London, G. ; European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine (EURECA‐m) Working Group of the European Renal Association ‐ European Dialysis Transplantation Association (ERA‐EDTA) . (2017) The systemic nature of CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 13, 344–358 - PubMed
-
- Levin, A. , Tonelli, M. , Bonventre, J. , Coresh, J. , Donner, J. A. , Fogo, A. B. , Fox, C. S. , Gansevoort, R. T. , Heerspink, H. J. L. , Jardine, M. , Kasiske, B. , Köttgen, A. , Kretzler, M. , Levey, A. S. , Luyckx, V. A. , Mehta, R. , Moe, O. , Obrador, G. , Pannu, N. , Parikh, C. R. , Perkovic, V. , Pollock, C. , Stenvinkel, P. , Tuttle, K. R. , Wheeler, D. C. , and Eckardt, K. U. ; ISN Global Kidney Health Summit participants . (2017) Global kidney health 2017 and beyond: a roadmap for closing gaps in care, research, and policy. Lancet 390, 1888–1917 - PubMed
-
- Liu, B. C. , Tang, T. T. , Lv, L. L. , and Lan, H. Y. (2018) Renal tubule injury: a driving force toward chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 93, 568–579 - PubMed
-
- Ishii, Y. , Hamashima, T. , Yamamoto, S. , and Sasahara, M. (2017) Pathogenetic significance and possibility as a therapeutic target of platelet derived growth factor. Pathol. Int. 67, 235–246 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

