A rare cutaneous phototoxic rash after vandetanib therapy in a patient with thyroid cancer: A case report
- PMID: 31374006
- PMCID: PMC6709084
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016392
A rare cutaneous phototoxic rash after vandetanib therapy in a patient with thyroid cancer: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Vandetanib is effective for treating symptomatic or progressive medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease, but its toxicity such as photosensitivity reactions should be considered. It is a rare adverse effect of this drug but might cause severe morbidity and even mortality.
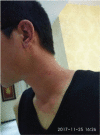
Patient concerns: A 26-year man with MTC developed phototoxic rashes on the sun-exposed areas of his shin after 15 days from the initiation of vandetanib treatment. Grade II skin toxicity was evaluated based on the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events standard.
Diagnoses: Drug-induced phototoxic rash.
Interventions: The vandetanib dose was reduced by 30%, and the application of topical steroids and sunscreen was adopted.
Outcomes: After dose reduction of vandetanib, the symptoms of vandetanib-induced phototoxic rash resolved, although residual pigmentation was observed.
Lessons: Close attention should be paid to the adverse effect of vandetanib, phototoxic rash, and patients should be advised on the prevention and treatment measures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Carlomagno F, Vitagliano D, Guida T, et al. ZD6474, an orally available inhibitor of KDR tyrosine kinase activity, efficiently blocks oncogenic RET kinases. Cancer Res 2002;62:7284. - PubMed
-
- http://www1.astrazeneca-us.com/pi/vandetanib.pdf [Accessed April 13, 2011].
-
- Yoh K, Seto T, Satouchi M, et al. Vandetanib in patients with previously treated RET-rearranged advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (LURET): an open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir Med 2017;5:42–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

