Modeling Monogenic Diabetes using Human ESCs Reveals Developmental and Metabolic Deficiencies Caused by Mutations in HNF1A
- PMID: 31374199
- PMCID: PMC6785828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.07.007
Modeling Monogenic Diabetes using Human ESCs Reveals Developmental and Metabolic Deficiencies Caused by Mutations in HNF1A
Abstract
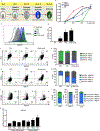
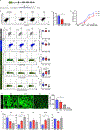
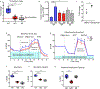
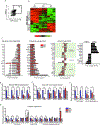
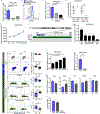
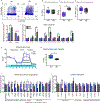
Human monogenic diabetes, caused by mutations in genes involved in beta cell development and function, has been a challenge to study because multiple mouse models have not fully recapitulated the human disease. Here, we use genome edited human embryonic stem cells to understand the most common form of monogenic diabetes, MODY3, caused by mutations in the transcription factor HNF1A. We found that HNF1A is necessary to repress an alpha cell gene expression signature, maintain endocrine cell function, and regulate cellular metabolism. In addition, we identified the human-specific long non-coding RNA, LINKA, as an HNF1A target necessary for normal mitochondrial respiration. These findings provide a possible explanation for the species difference in disease phenotypes observed with HNF1A mutations and offer mechanistic insights into how the HNF1A gene may also influence type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: HNF1A; MODY3; beta cells; cell respiration; diabetes; embryonic stem cells; glycolysis; long non-coding RNA; pancreas.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ainscow EK, Zhao C and Rutter G. a (2000). Acute overexpression of lactate dehydrogenase-A perturbs beta-cell mitochondrial metabolism and insulin secretion. Diabetes, 49(7), pp. 1149–1155. - PubMed
-
- Akpinar P, Kuwajima S, Krützfeldt J and Stoff el M (2005). Tmem27: a cleaved and shed plasma membrane protein that stimulates pancreatic beta cell proliferation. Cell metab, 2(6), pp. 385–97. - PubMed
-
- Brial F, Lussier CR, Belleville K, Sarret P and Boudreau F (2015). Ghrelin inhibition restores glucose homeostasis in hepatocyte nuclear factor-1a (MODY3)-deficient mice’, Diabetes, 64(9). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- UC4 DK104211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 DK094723/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK108120/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK118155/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK112232/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092113/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD086984/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK106755/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008396/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK104196/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000666/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

