Spatial and functional heterogeneity of follicular helper T cells in autoimmunity
- PMID: 31374450
- PMCID: PMC7255639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2019.06.005
Spatial and functional heterogeneity of follicular helper T cells in autoimmunity
Abstract
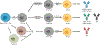
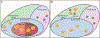
Follicular helper T cells provide signals that promote B cell development, proliferation, and production of affinity matured and appropriately isotype switched antibodies. In addition to their classical locations within B cell follicles and germinal centers therein, B cell helper T cells are also found in extrafollicular spaces - either in secondary lymphoid or non-lymphoid tissues. Both follicular and extrafollicular T helper cells drive autoantibody-mediated autoimmunity. Interfering with B cell help provided by T cells can ameliorate autoimmune disease in animal models and human patients. The next frontier in Tfh cell biology will be identification of Tfh cell-specific pathogenic changes in autoimmunity and exploiting them for therapeutic purposes.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests: None
Figures
References
-
- Vinuesa CG, Linterman MA, Goodnow CC, Randall KL: T cells and follicular dendritic cells in germinal center B-cell formation and selection. Immunol Rev 2010, 237:72–89. - PubMed
-
-
Song W, Craft J: T follicular helper cell heterogeneity: Time, space, and function. Immunol Rev 2019, 288:85–96.
•• This recent thorough review describes our current understanding of physiologic Tfh cell development and function.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

