Fucoxanthin and Rosmarinic Acid Combination Has Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in UVB-Exposed HaCaT Keratinocytes
- PMID: 31374828
- PMCID: PMC6722862
- DOI: 10.3390/md17080451
Fucoxanthin and Rosmarinic Acid Combination Has Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in UVB-Exposed HaCaT Keratinocytes
Abstract
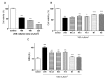
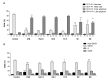
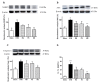
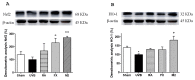
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the main risk factor to develop skin pathologies or cancer because it encourages oxidative condition and skin inflammation. In this sense, strategies for its prevention are currently being evaluated. Natural products such as carotenoids or polyphenols, which are abundant in the marine environment, have been used in the prevention of oxidative stress due to their demonstrated antioxidant activities. Nevertheless, the anti-inflammatory activity and its implication in photo-prevention have not been extensively studied. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the combination of fucoxanthin (FX) and rosmarinic acid (RA) on cell viability, apoptosis induction, inflammasome regulation, and anti-oxidative response activation in UVB-irradiated HaCaT keratinocytes. We demonstrated for the first time that the combination of FX and RA (5 µM RA plus 5 μM FX, designated as M2) improved antioxidant and anti-inflammatory profiles in comparison to compounds assayed individually, by reducing UVB-induced apoptosis and the consequent ROS production. Furthermore, the M2 combination modulated the inflammatory response through down-regulation of inflammasome components such as NLRP3, ASC, and Caspase-1, and the interleukin (IL)-1β production. In addition, Nrf2 and HO-1 antioxidant genes expression increased in UVB-exposed HaCaT cells pre-treated with M2. These results suggest that this combination of natural products exerts photo-protective effects by down-regulating NRLP3-inflammasome and increasing Nrf2 signalling pathway.
Keywords: NRLP3; UVB; anti-inflammatory; anti-oxidative; fucoxanthin; inflammasome; photo-protection; rosmarinic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prunella vulgaris extract and rosmarinic acid prevent UVB-induced DNA damage and oxidative stress in HaCaT keratinocytes.Arch Dermatol Res. 2010 Apr;302(3):171-81. doi: 10.1007/s00403-009-0999-6. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010. PMID: 19862537
-
Rutin and ascorbic acid cooperation in antioxidant and antiapoptotic effect on human skin keratinocytes and fibroblasts exposed to UVA and UVB radiation.Arch Dermatol Res. 2019 Apr;311(3):203-219. doi: 10.1007/s00403-019-01898-w. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Arch Dermatol Res. 2019. PMID: 30783768
-
Allicin attenuates UVB-induced photodamage of keratinocytes by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes and activating the PI3K/Akt pathway.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Dec 14;317(1):124. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03599-5. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39673634 Free PMC article.
-
Photoaging and skin cancer: Is the inflammasome the missing link?Mech Ageing Dev. 2018 Jun;172:131-137. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Mech Ageing Dev. 2018. PMID: 29545203 Review.
-
On a Beam of Light: Photoprotective Activities of the Marine Carotenoids Astaxanthin and Fucoxanthin in Suppression of Inflammation and Cancer.Mar Drugs. 2020 Oct 30;18(11):544. doi: 10.3390/md18110544. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33143013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Rosmarinic Acid-Loaded Nanovesicles in Acute Colitis through Modulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 26;11(2):162. doi: 10.3390/biom11020162. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33530569 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Potential Seaweed-Derived Bioactive Compounds for Pharmaceutical Applications.Mar Drugs. 2022 Feb 15;20(2):141. doi: 10.3390/md20020141. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35200670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Effects of Microalgal Carotenoids.Mar Drugs. 2021 Sep 23;19(10):531. doi: 10.3390/md19100531. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34677429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fucoxanthin@Polyvinylpyrrolidone Nanoparticles Promoted Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Death in Caco-2 Human Colon Cancer Cells.Mar Drugs. 2021 Feb 5;19(2):92. doi: 10.3390/md19020092. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33562511 Free PMC article.
-
Combined effects of quinic acid and isochlorogenic acid B on LPS-induced inflammation and pyroptosis in MAC-T cells and mouse mammary glands.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jun 5;12:1476302. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1476302. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40538727 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

