Mammalian DNA Polymerase Kappa Activity and Specificity
- PMID: 31374881
- PMCID: PMC6695781
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24152805
Mammalian DNA Polymerase Kappa Activity and Specificity
Abstract
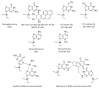
DNA polymerase (pol) kappa is a Y-family translesion DNA polymerase conserved throughout all domains of life. Pol kappa is special6 ized for the ability to copy DNA containing minor groove DNA adducts, especially N2-dG adducts, as well as to extend primer termini containing DNA damage or mismatched base pairs. Pol kappa generally cannot copy DNA containing major groove modifications or UV-induced photoproducts. Pol kappa can also copy structured or non-B-form DNA, such as microsatellite DNA, common fragile sites, and DNA containing G quadruplexes. Thus, pol kappa has roles both in maintaining and compromising genomic integrity. The expression of pol kappa is altered in several different cancer types, which can lead to genome instability. In addition, many cancer-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms have been reported in the POLK gene, some of which are associated with poor survival and altered chemotherapy response. Because of this, identifying inhibitors of pol kappa is an active area of research. This review will address these activities of pol kappa, with a focus on lesion bypass and cellular mutagenesis.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA replication; Y-family; chemotherapy resistance; primer extension; translesion DNA synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Gruz P., Pisani F.M., Shimizu M., Yamada M., Hayashi I., Morikawa K., Nohmi T. Synthetic activity of Sso DNA polymerase Y1, an archaeal DinB-like DNA polymerase, is stimulated by processivity factors proliferating cell nuclear antigen and replication factor C. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:47394–47401. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107213200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

