Pharmacokinetics of B-Ring Unsubstituted Flavones
- PMID: 31374885
- PMCID: PMC6723510
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11080370
Pharmacokinetics of B-Ring Unsubstituted Flavones
Abstract
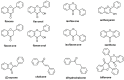
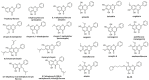
B-ring unsubstituted flavones (of which the most widely known are chrysin, baicalein, wogonin, and oroxylin A) are 2-phenylchromen-4-one molecules of which the B-ring is devoid of any hydroxy, methoxy, or other substituent. They may be found naturally in a number of herbal products used for therapeutic purposes, and several have been designed by researchers and obtained in the laboratory. They have generated interest in the scientific community for their potential use in a variety of pathologies, and understanding their pharmacokinetics is important for a grasp of their optimal use. Based on a comprehensive survey of the relevant literature, this paper examines their absorption (with deglycosylation as a preliminary step) and their fate in the body, from metabolism to excretion. Differences among species (inter-individual) and within the same species (intra-individual) variability have been examined based on the available data, and finally, knowledge gaps and directions of future research are discussed.
Keywords: B-ring unsubstituted flavones; baicalein; chrysin; oroxylin A; pharmacokinetics; wogonin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. R.A has received consultancy and speakers’ fees from various pharmaceutical companies. The companies had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral pharmacokinetics of baicalin, wogonoside, oroxylin A 7-O-β-d-glucuronide and their aglycones from an aqueous extract of Scutellariae Radix in the rat.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016 Jul 15;1026:124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.11.049. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26809374
-
Comparison of intestinal absorption and disposition of structurally similar bioactive flavones in Radix Scutellariae.AAPS J. 2012 Mar;14(1):23-34. doi: 10.1208/s12248-011-9310-9. Epub 2011 Dec 14. AAPS J. 2012. PMID: 22167378 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Uptake of Bioactive Flavones in Scutellariae Radix and Its Relationship to Anxiolytic Effect in Mice.Mol Pharm. 2017 Sep 5;14(9):2908-2916. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00029. Epub 2017 May 1. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28426226
-
Pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics properties of Radix Scutellariae and its bioactive flavones.Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2011 Nov;32(8):427-45. doi: 10.1002/bdd.771. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2011. PMID: 21928297 Review.
-
[Study advance in biosynthesis of flavone from Scutellaria].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Oct;45(20):4819-4826. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200709.601. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33350252 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Borcalein: a Carborane-Based Analogue of Baicalein with 12-Lipoxygenase-Independent Toxicity.ChemMedChem. 2022 Jan 5;17(1):e202100588. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100588. Epub 2021 Nov 11. ChemMedChem. 2022. PMID: 34694057 Free PMC article.
-
Abundant Extractable Metabolites from Temperate Tree Barks: The Specific Antimicrobial Activity of Prunus Avium Extracts.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Mar 4;9(3):111. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9030111. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32143394 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Studies of Flavone-DENV E-3 Protein-SWCNT Interaction at the Flavonoid Binding Sites.Viruses. 2025 Apr 4;17(4):525. doi: 10.3390/v17040525. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40284968 Free PMC article.
-
Current biological and pharmacological updates on wogonin.EXCLI J. 2020 May 13;19:635-640. eCollection 2020. EXCLI J. 2020. PMID: 32536834 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
From micro to macro, nanotechnology demystifies acute pancreatitis: a new generation of treatment options emerges.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jan 29;23(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03106-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39881355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Markham K.R., Porter L.J. Flavonoids in the green algae (chlorophyta) Phytochemistry. 1969;8:1777–1781. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)85968-3. - DOI
-
- Ben Saad H., Gargouri M., Kallel F., Chaabene R., Boudawara T., Jamoussi K., Magné C., Mounir Zeghal K., Hakim A., Ben Amara I. Flavonoid compounds from the red marine alga Alsidium corallinum protect against potassium bromate-induced nephrotoxicity in adult mice: Alsidium corallinum protect against KBrO3-induced nephrotoxicity. Environ. Toxicol. 2017;32:1475–1486. doi: 10.1002/tox.22368. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

