Antibacterial Activity and Molecular Docking Studies of a Selected Series of Hydroxy-3-arylcoumarins
- PMID: 31375003
- PMCID: PMC6696357
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24152815
Antibacterial Activity and Molecular Docking Studies of a Selected Series of Hydroxy-3-arylcoumarins
Abstract
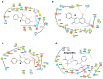
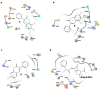
Antibiotic resistance is one of the main public health concerns of this century. This resistance is also associated with oxidative stress, which could contribute to the selection of resistant bacterial strains. Bearing this in mind, and considering that flavonoid compounds are well known for displaying both activities, we investigated a series of hydroxy-3-arylcoumarins with structural features of flavonoids for their antibacterial activity against different bacterial strains. Active compounds showed selectivity against the studied Gram-positive bacteria compared to Gram-negative bacteria. 5,7-Dihydroxy-3-phenylcoumarin (compound 8) displayed the best antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 11 g/mL, followed by Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA strain) and Listeria monocytogenes with MICs of 22 and 44 g/mL, respectively. Moreover, molecular docking studies performed on the most active compounds against Staphylococcus aureus tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase and topoisomerase II DNA gyrase revealed the potential binding mode of the ligands to the site of the appropriate targets. Preliminary structure-activity relationship studies showed that the antibacterial activity can be modulated by the presence of the 3-phenyl ring and by the position of the hydroxyl groups at the coumarin scaffold.
Keywords: Perkin–Oglialoro reaction; antibacterial activity; hydroxy-3-arylcoumarins; molecular docking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

