Class IIa HDACs regulate learning and memory through dynamic experience-dependent repression of transcription
- PMID: 31375688
- PMCID: PMC6677776
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11409-0
Class IIa HDACs regulate learning and memory through dynamic experience-dependent repression of transcription
Abstract
The formation of new memories requires transcription. However, the mechanisms that limit signaling of relevant gene programs in space and time for precision of information coding remain poorly understood. We found that, during learning, the cellular patterns of expression of early response genes (ERGs) are regulated by class IIa HDACs 4 and 5, transcriptional repressors that transiently enter neuronal nuclei from cytoplasm after sensory input. Mice lacking these repressors in the forebrain have abnormally broad experience-dependent expression of ERGs, altered synaptic architecture and function, elevated anxiety, and severely impaired memory. By acutely manipulating the nuclear activity of class IIa HDACs in behaving animals using a chemical-genetic technique, we further demonstrate that rapid induction of transcriptional programs is critical for memory acquisition but these programs may become dispensable when a stable memory is formed. These results provide new insights into the molecular basis of memory storage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
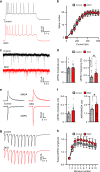
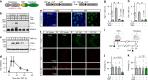
Similar articles
-
Nuclear calcium signaling regulates nuclear export of a subset of class IIa histone deacetylases following synaptic activity.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8074-8084. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.432773. Epub 2013 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23364788 Free PMC article.
-
Class IIa HDACs - new insights into their functions in physiology and pathology.FEBS J. 2015 May;282(9):1736-44. doi: 10.1111/febs.13061. Epub 2014 Oct 27. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25244360 Review.
-
beta-Amyloid disrupts activity-dependent gene transcription required for memory through the CREB coactivator CRTC1.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 14;30(28):9402-10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2154-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20631169 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Functional Characterization of Histone Deacetylase 4 (HDAC4).Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1436:31-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3667-0_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27246207
-
A role for histone deacetylases in the cellular and behavioral mechanisms underlying learning and memory.Learn Mem. 2014 Sep 16;21(10):564-8. doi: 10.1101/lm.036012.114. Print 2014 Oct. Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 25227251 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Role of HDACs in Regeneration and Ageing in the Peripheral Nervous System: Repair Schwann Cells as Pivotal Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 10;23(6):2996. doi: 10.3390/ijms23062996. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in transcriptional and translational regulation underlying long-term synaptic plasticity and memory.Learn Mem. 2019 Aug 15;26(9):307-317. doi: 10.1101/lm.048769.118. Print 2019 Sep. Learn Mem. 2019. PMID: 31416904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Memory Component of Alzheimer's Disease: Biological Processes and Pathways across Brain Regions.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 6;12(2):263. doi: 10.3390/biom12020263. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204764 Free PMC article.
-
The role of nuclear Ca2+ in maintaining neuronal homeostasis and brain health.J Cell Sci. 2021 Apr 15;134(8):jcs254904. doi: 10.1242/jcs.254904. Epub 2021 Apr 22. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 33912918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC4 Inhibitors as Antivascular Senescence Therapeutics.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jun 29;2022:3087916. doi: 10.1155/2022/3087916. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35814270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

