Technique, protocols and adverse reactions for contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM): a systematic review
- PMID: 31376021
- PMCID: PMC6677840
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-019-0756-0
Technique, protocols and adverse reactions for contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM): a systematic review
Abstract
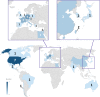
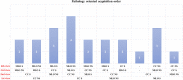
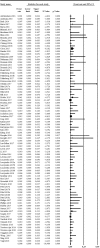
We reviewed technical parameters, acquisition protocols and adverse reactions (ARs) for contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM). A systematic search in databases, including MEDLINE/EMBASE, was performed to extract publication year, country of origin, study design; patients; mammography unit/vendor, radiation dose, low-/high-energy tube voltage; contrast molecule, concentration and dose; injection modality, ARs and acquisition delay; order of views; examination time. Of 120 retrieved articles, 84 were included from 22 countries (September 2003-January 2019), totalling 14012 patients. Design was prospective in 44/84 studies (52%); in 70/84 articles (83%), a General Electric unit with factory-set kVp was used. Per-view average glandular dose, reported in 12/84 studies (14%), ranged 0.43-2.65 mGy. Contrast type/concentration was reported in 79/84 studies (94%), with Iohexol 350 mgI/mL mostly used (25/79, 32%), dose and flow rate in 72/84 (86%), with 1.5 mL/kg dose at 3 mL/s in 62/72 studies (86%). Injection was described in 69/84 articles (82%), automated in 59/69 (85%), manual in 10/69 (15%) and flush in 35/84 (42%), with 10-30 mL dose in 19/35 (54%). An examination time < 10 min was reported in 65/84 studies (77%), 120 s acquisition delay in 65/84 (77%) and order of views in 42/84 (50%) studies, beginning with the craniocaudal view of the non-suspected breast in 7/42 (17%). Thirty ARs were reported by 14/84 (17%) studies (26 mild, 3 moderate, 1 severe non-fatal) with a pooled rate of 0.82% (fixed-effect model). Only half of CESM studies were prospective; factory-set kVp, contrast 1.5 mL/kg at 3 mL/s and 120 s acquisition delay were mostly used; only 1 severe AR was reported. CESM protocol standardisation is advisable.
Keywords: Breast; Contrast media; Drug-related side effects and adverse reactions; Mammography; Radiation dosage.
Conflict of interest statement
FS declares to have received grants from or to be member of speakers’ bureau/advisory board for Bayer, Bracco, and General Electric. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Frigerio Alfonso, Sardanelli Francesco, Podo Franca. Breast Cancer. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2017. Radiological Screening of Breast Cancer: Evolution; pp. 171–203.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

