Elevation of casein kinase 1ε associated with TDP-43 and tau pathologies in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 31376192
- PMCID: PMC8018014
- DOI: 10.1111/bpa.12775
Elevation of casein kinase 1ε associated with TDP-43 and tau pathologies in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
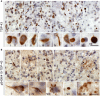
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the presence of extracellular amyloid β plaques and intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles of hyperphosphorylated microtubule-associated protein tau in the brain. Aggregation of transactive response DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) in the neuronal cytoplasm is another feature of AD. However, how TDP-43 is associated with AD pathogenesis is unknown. Here, we found that casein kinase 1ε (CK1ε) phosphorylated TDP-43 at Ser403/404 and Ser409/410. In AD brains, the level of CK1ε was dramatically increased and positively correlated with the phosphorylation of TDP-43 at Ser403/404 and Ser409/410. Overexpression of CK1ε promoted its cytoplasmic aggregation and suppressed TDP-43-promoted tau mRNA instability and tau exon 10 inclusion, leading to an increase of tau and 3R-tau expressions. Levels of CK1ε and TDP-43 phosphorylation were positively correlated with the levels of total tau and 3R-tau in human brains. Furthermore, we observed, in pilot immunohistochemical studies, that the severe tau pathology was accompanied by robust TDP-43 pathology and a high level of CK1ε. Taken together, our findings suggest that the elevation of CK1ε in AD brain may phosphorylate TDP-43, promote its cytoplasmic aggregation and suppress its function in tau mRNA processing, leading to acceleration/exacerbation of tau pathology. Thus, the elevation of CK1ε may link TDP-43 to tau pathogenesis in AD brain.
Keywords: CK1ε; TDP-43; TDP-43 proteinopathy; phosphorylation; tau; tau pathology.
© 2019 International Society of Neuropathology.
Figures





References
-
- Alafuzoff I, Iqbal K, Friden H, Adolfsson R, Winblad B (1987) Histopathological criteria for progressive dementia disorders: clinical‐pathological correlation and classification by multivariate data analysis. Acta Neuropathol 74:209–225. - PubMed
-
- Andorfer C, Kress Y, Espinoza M, de Silva R, Tucker KL, Barde YA et al (2003) Hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of tau in mice expressing normal human tau isoforms. J Neurochem 86:582–590. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H et al (2006) TDP‐43 is a component of ubiquitin‐positive tau‐negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 351:602–611. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Mackenzie IR, Hasegawa M, Nonoka T, Niizato K, Tsuchiya K et al (2009) Phosphorylated TDP‐43 in Alzheimer's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol 117:125–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

