Androgenic Effects on Ventricular Repolarization: A Translational Study From the International Pharmacovigilance Database to iPSC-Cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 31378084
- PMCID: PMC6756939
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040162
Androgenic Effects on Ventricular Repolarization: A Translational Study From the International Pharmacovigilance Database to iPSC-Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
Background: Male hypogonadism, arising from a range of etiologies including androgen-deprivation therapies (ADTs), has been reported as a risk factor for acquired long-QT syndrome (aLQTS) and torsades de pointes (TdP). A full description of the clinical features of aLQTS associated with ADT and of underlying mechanisms is lacking.
Methods: We searched the international pharmacovigilance database VigiBase for men (n=6 560 565 individual case safety reports) presenting with aLQTS, TdP, or sudden death associated with ADT. In cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from men, we studied electrophysiological effects of ADT and dihydrotestosterone.
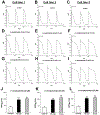
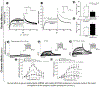
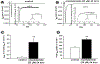
Results: Among subjects receiving ADT in VigiBase, we identified 184 cases of aLQTS (n=168) and/or TdP (n=68; 11% fatal), and 99 with sudden death. Of the 10 ADT drugs examined, 7 had a disproportional association (reporting odds ratio=1.4-4.7; P<0.05) with aLQTS, TdP, or sudden death. The minimum and median times to sudden death were 0.25 and 92 days, respectively. The androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide was associated with more deaths (5430/31 896 [17%]; P<0.0001) than other ADT used for prostate cancer (4208/52 089 [8.1%]). In induced pluripotent stem cells, acute and chronic enzalutamide (25 µM) significantly prolonged action potential durations (action potential duration at 90% when paced at 0.5 Hz; 429.7±27.1 (control) versus 982.4±33.2 (acute, P<0.001) and 1062.3±28.9 ms (chronic; P<0.001), and generated afterdepolarizations and/or triggered activity in drug-treated cells (11/20 acutely and 8/15 chronically). Enzalutamide acutely and chronically inhibited delayed rectifier potassium current, and chronically enhanced late sodium current. Dihydrotestosterone (30 nM) reversed enzalutamide electrophysiological effects on induced pluripotent stem cells.
Conclusions: QT prolongation and TdP are a risk in men receiving enzalutamide and other ADTs.
Clinical trial registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT03193138.
Keywords: androgen antagonists; hypogonadism; long QT syndrome; testosterone; torsades de pointes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
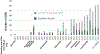

Comment in
-
Letter by Chen et al Regarding Article, "Androgenic Effects on Ventricular Repolarization: A Translational Study From the International Pharmacovigilance Database to iPSC-Cardiomyocytes".Circulation. 2020 Feb 4;141(5):e61-e62. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.043362. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32011924 No abstract available.
-
Response by Salem et al to Letter Regarding Article, "Androgenic Effects on Ventricular Repolarization: A Translational Study From the International Pharmacovigilance Database to iPSC-Cardiomyocytes".Circulation. 2020 Feb 4;141(5):e63-e64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.045215. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32011925 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Roden DM. Drug-induced prolongation of the QT interval. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1013–1022. - PubMed
-
- Malfatto G, Beria G, Sala S, Bonazzi O and Schwartz PJ. Quantitative analysis of T wave abnormalities and their prognostic implications in the idiopathic long QT syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994;23:296–301. - PubMed
-
- Yang T, Snyders D and Roden DM. Drug block of I(kr): model systems and relevance to human arrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2001;38:737–744. - PubMed
-
- Takenaka K, Ai T, Shimizu W, Kobori A, Ninomiya T, Otani H, Kubota T, Takaki H, Kamakura S and Horie M. Exercise stress test amplifies genotype-phenotype correlation in the LQT1 and LQT2 forms of the long-QT syndrome. Circulation. 2003;107:838–844. - PubMed
-
- Graff C, Struijk JJ, Matz J, Kanters JK, Andersen MP, Nielsen J and Toft E. Covariate analysis of QTc and T-wave morphology: new possibilities in the evaluation of drugs that affect cardiac repolarization. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;88:88–94. - PubMed

