Cell Mass Increase Associated with Formation of Glucose-Controlling β-Cell Mass in Device-Encapsulated Implants of hiPS-Derived Pancreatic Endoderm
- PMID: 31379140
- PMCID: PMC6877770
- DOI: 10.1002/sctm.19-0043
Cell Mass Increase Associated with Formation of Glucose-Controlling β-Cell Mass in Device-Encapsulated Implants of hiPS-Derived Pancreatic Endoderm
Abstract
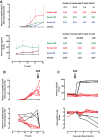
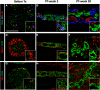
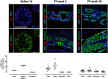
Device-encapsulated human stem cell-derived pancreatic endoderm (PE) can generate functional β-cell implants in the subcutis of mice, which has led to the start of clinical studies in type 1 diabetes. Assessment of the formed functional β-cell mass (FBM) and its correlation with in vivo metabolic markers can guide clinical translation. We recently reported ex vivo characteristics of device-encapsulated human embryonic stem cell-derived (hES)-PE implants in mice that had established a metabolically adequate FBM during 50-week follow-up. Cell suspensions from retrieved implants indicated a correlation with the number of formed β cells and their maturation to a functional state comparable to human pancreatic β cells. Variability in metabolic outcome was attributed to differences in number of PE-generated β cells. This variability hinders studies on processes involved in FBM-formation. This study reports modifications that reduce variability. It is undertaken with device-encapsulated human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived-PE subcutaneously implanted in mice. Cell mass of each cell type was determined on intact tissue inside the device to obtain more precise data than following isolation and dispersion. Implants in a preformed pouch generated a glucose-controlling β-cell mass within 20 weeks in over 60% of recipients versus less than 20% in the absence of a pouch, whether the same or threefold higher cell dose had been inserted. In situ analysis of implants indicated a role for pancreatic progenitor cell expansion and endocrine differentiation in achieving the size of β- and α-cell mass that correlated with in vivo markers of metabolic control. Stem Cells Translational Medicine 2019;8:1296&1305.
Keywords: Cell transplantation; Diabetes; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Pancreatic differentiation; Progenitor cells.
© 2019 The Authors. Stem Cells Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
T.R. is Ph.D. fellow of Research Foundation Flanders‐FWO. The other authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kroon E, Martinson LA, Kadoya K et al. Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose‐responsive insulin‐secreting cells in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 2008;26:443–452. - PubMed
-
- Motté E, Szepessy E, Suenens K et al. Composition and function of macroencapsulated human embryonic stem cell‐derived implants: Comparison with clinical human islet cell grafts. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2014;307:E838–E846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

