Regulation of Eicosanoid Pathways by MicroRNAs
- PMID: 31379585
- PMCID: PMC6659501
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00824
Regulation of Eicosanoid Pathways by MicroRNAs
Abstract
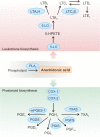
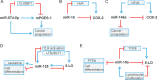
Over the last years, many microRNAs (miRNAs) have been identified that regulate the formation of bioactive lipid mediators such as prostanoids and leukotrienes. Many of these miRNAs are involved in complex regulatory circuits necessary for the fine-tuning of biological functions including inflammatory processes or cell growth. A better understanding of these networks will contribute to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer. In this review, we provide an overview of the current knowledge of miRNA regulation in eicosanoid pathways with special focus on novel miRNA functions and regulatory circuits of leukotriene and prostaglandin biosynthesis.
Keywords: eicosanoids; inflammation; microRNA; new miRNA functions; prostaglandins.
Figures

References
-
- Cong R., Tao K., Fu P., Lou L., Zhu Y., Chen S., et al. (2017). MicroRNA218 promotes prostaglandin E2 to inhibit osteogenic differentiation in synovial mesenchymal stem cells by targeting 15hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase [NAD(+)]. Mol. Med. Rep. 16, 9347–9354. 10.3892/mmr.2017.7795 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

