CrERF5, an AP2/ERF Transcription Factor, Positively Regulates the Biosynthesis of Bisindole Alkaloids and Their Precursors in Catharanthus roseus
- PMID: 31379908
- PMCID: PMC6657538
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00931
CrERF5, an AP2/ERF Transcription Factor, Positively Regulates the Biosynthesis of Bisindole Alkaloids and Their Precursors in Catharanthus roseus
Abstract
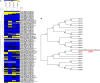
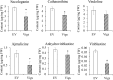
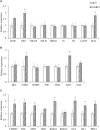
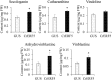
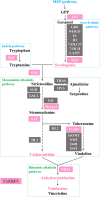
Catharanthus roseus contains a variety of monoterpenoid indole alkaloids (MIAs), among which bisindole alkaloids vinblastine and vincristine are well-known to have antitumor effects and widely used in clinical treatment. However, their contents in C. roseus is extremely low and difficult to meet market demands. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the transcriptional regulation mechanism of MIAs biosynthesis for high yielding of bisindole alkaloids in C. roseus. Studies have shown that MIAs biosynthesis in C. roseus has complex temporal and spacial specificity and is under tight transcriptional regulation, especially bisindole alkaloids. In this study, an AP2/ERF transcription factor CrERF5 was selected by RNA-seq of C. roseus organs, and its full-length sequence was cloned and characterized. CrERF5 responds to both ethylene and JA signals and is localized in the nucleus. CrERF5 could activate the transcriptional activity of the TDC promoter. Transient overexpressing CrERF5 in C. roseus petals caused a significant increase of the expression levels of key genes in both the upstream and downstream pathways of MIAs biosynthesis while silencing CrERF5 resulted in a decrease of them. Accordingly, the contents of bisindole alkaloids anhydrovinblastine and vinblastine, monoindole alkaloids ajmalicine, vindoline, and catharanthine were strongly enhanced in CrERF5-overexpressing petals while their contents decreased in CrERF5-silenced plants. These results suggested that CrERF5 is a novel positive ethylene-JA-inducible AP2/ERF transcription factor upregulating the MIAs biosynthetic pathway leading to the bisindole alkaloids accumulation.
Keywords: AP2/ERF transcription factor; Catharanthus roseus; MIAs biosynthesis; bisindole alkaloids; transcriptional regulation.
Figures

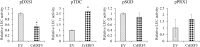

References
-
- Charlton W. L., Matsui K., Johnson B., Graham I. A., Ohme-Takagi M., Baker A. (2005). Salt-induced expression of peroxisome-associated genes requires components of the ethylene, jasmonate and abscisic acid signalling pathways. Plant Cell Environ. 28 513–524. 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01293.x - DOI
-
- Chatel G., Montiel G., Pré M., Memelink J., Thiersault M., Saint-Pierre B., et al. (2003). CrMYC1, a Catharanthus roseus elicitor-and jasmonate-responsive bHLH transcription factor that binds the G-box element of the strictosidine synthase gene promoter. J. Exp. Bot 54 2587–2588. 10.1093/jxb/erg275 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen Q., Wu K., Tang Z., Guo Q. X., Guo X., Wang H. (2017). Exogenous ethylene enhanced the cadmium resistance and changed the alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus seedlings. Acta Physiol. Plant 39:267.
-
- Costa M. M. R., Hilliou F., Duarte P., Pereira L. G., Almeida I., Leech M., et al. (2008). Molecular cloning and characterization of a vacuolar class III peroxidase involved in the metabolism of anticancer alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiol. 146 403–417. 10.1104/pp.107.107060 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

