Human-Derived Corneal Epithelial Cells Expressing Cell Cycle Regulators as a New Resource for in vitro Ocular Toxicity Testing
- PMID: 31379915
- PMCID: PMC6646426
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00587
Human-Derived Corneal Epithelial Cells Expressing Cell Cycle Regulators as a New Resource for in vitro Ocular Toxicity Testing
Abstract
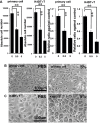
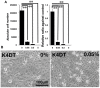
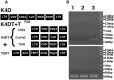
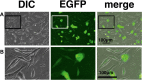
The Draize test has been used on rabbits since the 1960s to evaluate the irritation caused by commercial chemicals in products such as cosmetics or hairdressing products. However, since 2003, such tests, including the Draize test for cosmetics, have been prohibited in European countries because they are considered problematic to animal welfare. For this reason, replacement of in vivo methods with the alternative in vitro methods has become an important goal. In this study, we established a corneal epithelial cell line co-expressing a mutant cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), Cyclin D1, and telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT). The established cell line maintained its original morphology and had an enhanced proliferation rate. Furthermore, the cells showed a significant, dose-dependent decrease in viability in an irritation test using glycolic acid and Benzalkonium chloride. These cells can now be shared with toxicology scientists and should contribute to increasing the reproducibility of chemical testing in vitro.
Keywords: cell cycle regulators; corneal epithelial cells; cyclin D1; cyclin-dependent kinase 4; immortalization; telomerase reverse transcriptase.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Immortalization of cells derived from domestic dogs through expressing mutant cyclin-dependent kinase 4, cyclin D1, and telomerase reverse transcriptase.Cytotechnology. 2022 Feb;74(1):181-192. doi: 10.1007/s10616-021-00504-0. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Cytotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35185293 Free PMC article.
-
Immortalization of Fetal Bovine Colon Epithelial Cells by Expression of Human Cyclin D1, Mutant Cyclin Dependent Kinase 4, and Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase: An In Vitro Model for Bacterial Infection.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 1;10(12):e0143473. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143473. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26624883 Free PMC article.
-
Cosmetics Europe compilation of historical serious eye damage/eye irritation in vivo data analysed by drivers of classification to support the selection of chemicals for development and evaluation of alternative methods/strategies: the Draize eye test Reference Database (DRD).Arch Toxicol. 2017 Feb;91(2):521-547. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1679-x. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 26997338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstituted human corneal epithelium: a new alternative to the Draize eye test for the assessment of the eye irritation potential of chemicals and cosmetic products.Toxicol In Vitro. 2006 Jun;20(4):499-512. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2005.09.005. Epub 2005 Oct 21. Toxicol In Vitro. 2006. PMID: 16243479
-
Amended final report on the safety assessment of glyceryl dilaurate, glyceryl diarachidate, glyceryl dibehenate, glyceryl dierucate, glyceryl dihydroxystearate, glyceryl diisopalmitate, glyceryl diisostearate, glyceryl dilinoleate, glyceryl dimyristate, glyceryl dioleate, glyceryl diricinoleate, glyceryl dipalmitate, glyceryl dipalmitoleate, glyceryl distearate, glyceryl palmitate lactate, glyceryl stearate citrate, glyceryl stearate lactate, and glyceryl stearate succinate.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 3:1-30. doi: 10.1080/10915810701663143. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 18273450 Review.
Cited by
-
The transcriptome of wild-type and immortalized corneal epithelial cells.Sci Data. 2021 May 7;8(1):126. doi: 10.1038/s41597-021-00908-9. Sci Data. 2021. PMID: 33963195 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a Robust and Simple Corneal Organ Culture Model to Monitor Wound Healing.J Clin Med. 2021 Aug 6;10(16):3486. doi: 10.3390/jcm10163486. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34441782 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of human airway epithelial cells with doxycycline-inducible cell growth and fluorescence reporters.Cytotechnology. 2021 Aug;73(4):555-569. doi: 10.1007/s10616-021-00477-0. Epub 2021 May 26. Cytotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34349346 Free PMC article.
-
Immortalized Canine Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Maintain the Immunomodulatory Capacity of the Original Primary Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 14;24(24):17484. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417484. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139314 Free PMC article.
-
Immortalization of cells derived from domestic dogs through expressing mutant cyclin-dependent kinase 4, cyclin D1, and telomerase reverse transcriptase.Cytotechnology. 2022 Feb;74(1):181-192. doi: 10.1007/s10616-021-00504-0. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Cytotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35185293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buehler E. V., Newman E. A. (1964). A comparison of eye irritation in monkey and rabbits. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 6, 701–710. - PubMed
-
- Donai K., Kiyono T., Eitsuka T., Guo Y., Kuroda K., Sone H., et al. (2014). Bovine and porcine fibroblasts can be immortalized with intact karyotype by the expression of mutant cyclin dependent kinase 4, cyclin D, and telomerase. J. Biotechnol. 176, 50–57. 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.02.017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duensing S., Lee L. Y., Duensing A., Basile J., Piboonniyom S., Gonzalez S., et al. (2000). The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins cooperate to induce mitotic defects and genomic instability by uncoupling centrosome duplication from the cell division cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 97, 10002–10007. 10.1073/pnas.170093297 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fukuda T., Eitsuka T., Donai K., Kurita M., Saito T., Okamoto H., et al. . (2018). Expression of human mutant cyclin dependent kinase 4, Cyclin D and telomerase extends the life span but does not immortalize fibroblasts derived from loggerhead sea turtle (Caretta caretta). Sci. Rep. 8:9229. 10.1038/s41598-018-27271-x, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

