Circulating MicroRNAs in Cancer: Potential and Challenge
- PMID: 31379918
- PMCID: PMC6656856
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00626
Circulating MicroRNAs in Cancer: Potential and Challenge
Abstract
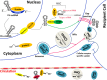
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous non-coding small RNA molecules that can be secreted into the circulation and exist in remarkably stable forms. Like intercellular miRNAs, circulating miRNAs participate in numerous regulations of biological process and expressed aberrantly under abnormal or pathological status. The quality and quantity changes of circulating miRNAs are associated with the initiation and progression of cancer and can be easily detected by basic molecular biology techniques. Consequently, considerable effort has been devoted to identify suitable extracellular miRNAs for noninvasive biomarkers in cancer. However, several challenges need to be overcome before the practical application. In this review, we discuss several issues of circulating miRNAs: biological function and basic transport carriers; extracellular cell communication process; roles as reliable cancer biomarkers and usage in targeted cancer therapy; and challenges for clinical application.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; challenge; circulating; communication; miRNAs; therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating miRNAs: roles in cancer diagnosis, prognosis and therapy.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Jan;81:75-93. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 25220354 Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in cancer diagnosis.Life Sci. 2020 May 1;248:117473. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117473. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32114007 Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: the advantage and disadvantage.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Apr 23;10:59. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0492-1. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29713393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biology of circulating microRNAs in cardiovascular disease.Eur J Clin Invest. 2015 Aug;45(8):860-74. doi: 10.1111/eci.12475. Eur J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26046787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Infectious Disease.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 16;8:118. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00118. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28261201 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease.Cells. 2022 Nov 10;11(22):3551. doi: 10.3390/cells11223551. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36428980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coding, or non-coding, that is the question.Cell Res. 2024 Sep;34(9):609-629. doi: 10.1038/s41422-024-00975-8. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39054345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology: A Promising Approach for Cancer Diagnosis, Therapeutics and Theragnosis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Aug 26;17:3735-3749. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S378074. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36051353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Promise of Liquid Biopsy to Predict Response to Immunotherapy in Metastatic Melanoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 18;11:645069. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.645069. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33816298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathway Analysis of Selected Circulating miRNAs in Plasma of Breast Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 2;21(19):7288. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197288. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33023154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arroyo J. D., Chevillet J. R., Kroh E. M., Ruf I. K., Prichard C. C., Gibson D. F., et al. (2011). Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (12), 5003–5008. 10.1073/pnas.1019055108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

