Increased Circulating Chemerin in Relation to Chronic Microvascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 31379940
- PMCID: PMC6662434
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8693516
Increased Circulating Chemerin in Relation to Chronic Microvascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is a global epidemic and increases mortality due to its vascular complications. Chemerin has been found to exert a major role in glucose and lipid metabolism. The aim of this study was to explore the correlation between plasma chemerin levels and microangiopathy in patients with T2DM.
Methods: A total of 598 T2DM patients were classified into two groups: with and without microvascular complications. Anthropometric parameters and blood pressure were taken. The amounts of glycosylated hemoglobin, glucose, lipid profiles, creatinine, and chemerin concentrations in the blood were determined. The presence and severity of nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy were also evaluated by specific tests.
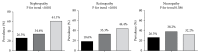
Results: Plasma levels of chemerin in diabetic subjects with microvascular complications were markedly elevated compared to those without. The number of microvascular complications increased with high plasma chemerin levels. Patients with high chemerin levels had an increased incidence of nephropathy and retinopathy. Furthermore, the chemerin plasma concentrations increased with the progression of diabetic nephropathy with highest values in macroalbuminuria groups. In contrast, no significant difference was observed in plasma chemerin levels between subjects with and without peripheral neuropathy. Pearson correlation analysis showed that plasma chemerin levels were positively related to duration of diabetes, serum creatinine, and 24-hour urine albumin excretion, even after multiple adjustments. Using logistic regression analysis, plasma chemerin concentrations were independently associated with the presence of nephropathy and retinopathy, not neuropathy.
Conclusion: This study elucidated a positive correlation between increased chemerin levels and the development of some subtypes of diabetic microangiopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Determinants and Stratification of Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Cureus. 2023 Aug 29;15(8):e44348. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44348. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37779807 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Serum Chemerin Levels in Diabetic Retinopathy of Type 2 Diabetic Patients.Curr Eye Res. 2016;41(1):114-20. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2015.1004718. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Curr Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 25848840
-
Relationship of plasma level of chemerin and vaspin to early atherosclerotic changes and cardiac autonomic neuropathy in adolescent type 1 diabetic patients.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Mar;28(3-4):265-73. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2014-0215. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25210758
-
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes using Hemoglobin A1c: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic cutpoint based on microvascular complications.Acta Diabetol. 2021 Mar;58(3):279-300. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01606-5. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Acta Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33141338 Free PMC article.
-
Incretins and microvascular complications of diabetes: neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy and microangiopathy.Diabetologia. 2023 Oct;66(10):1832-1845. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-05988-3. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Diabetologia. 2023. PMID: 37597048 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Chemerin-CMKLR1 Axis is Functionally important for Central Regulation of Energy Homeostasis.Front Physiol. 2022 May 30;13:897105. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.897105. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35711300 Free PMC article.
-
Chemerin in Participants with or without Insulin Resistance and Diabetes.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 22;12(4):924. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040924. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672278 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial Hypertension: Novel Pharmacological Targets and Future Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 4;13(19):5927. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195927. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39407987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum chemerin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: can it unravel the Chimera of concomitant type 2 diabetes?Reumatologia. 2020;58(4):257. doi: 10.5114/reum.2020.98439. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Reumatologia. 2020. PMID: 32921834 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid could attenuate the effect of chemerin-induced diabetic nephropathy progression.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021 Aug;24(8):1107-1116. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2021.50792.11570. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34804428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Report on Diabetes, World Health Organization, Geneva, 2016, http://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/
-
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF) (2017) IDF Diabetes Atlas, 8th Edition, International Diabetes Federation, Brussels, http://www.diabetesatlas.org/resources/2017-atlas.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

