Evaluation of the Biological Effects of Lyophilized Hydrophilic Extract of Rhus coriaria on Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity, Wound Healing, and Microbial Infections of Skin Wound Tissues
- PMID: 31379964
- PMCID: PMC6662417
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/5861537
Evaluation of the Biological Effects of Lyophilized Hydrophilic Extract of Rhus coriaria on Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity, Wound Healing, and Microbial Infections of Skin Wound Tissues
Abstract
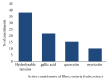
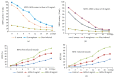
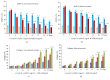
Impaired wound healing was mainly associated with severe microbial infections which significantly affect diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Thus, in this study, the potential wound healing activity, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activity of an aqueous extract of Rhus coriaria extract (AERc) were evaluated by wound contraction, scar formation, period of epithelization, MPO enzyme activity, collagenase-2 (MMP-8), hydroxyproline (HPX), and collagen deposition as markers of wound healing at different days of postwound. Phytoconstituents, microbial activity, and fibrogenic markers were screened by HPLC, disc-diffusion, and colorimetric assays. The animals were treated with Rhus coriaria extract (AERc) concentrations at doses of 5 mg.kg-1and 10 mg.kg-1, respectively. On days 6 and 9, the AERc-treated animals at doses of 5 mg.mL-1 and 10 mg.mL-1 exhibited a significant reduction in the wound area, increased deposition of collagen, HPX, and reduction in MMP-8, and MPO enzyme activity when compared with controls. Scar formation and epithelization were completed in 10 days compared to controls. In addition, in wounds infected separately with Staph. aureus or P. aeruginosa, the AERc extract significantly improved wound contraction, deposition of collagen, and HPx and reduced MMP-8 and MPO concentrations, with complete epithelization of wounds in 10-13 days compared to the saline-treated group. Hydrolyzable tannins, gallic acid, quercetin, and myricetin were the most common active components of AERc. In vitro, the AERc and its components were effective against a set of microbes especially Staph. aureus, P. aeruginosa, and Staph. aureus (MRSA). In conclusion, the results showed that antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activity of Rhus coriaria extract suggested its importance as a target for formulation of novel drugs against many microbial infections with minimal side effects and could play a good potential role in accelerating wound healing activity via promoting myofibroblast activity, increase of hydroxyproline and collagen deposition, and regulation of MMP-8 and MPO enzyme activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University through Vice Deanship of Scientific Research Chairs. The funding body played no role in the study design, manuscript writing, or decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Rhus coriaria L. methanolic fruit extract on wound healing in diabetic and non-diabetic rats.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 Aug;21(8):3567-3577. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14668. Epub 2021 Dec 20. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34928525
-
Mallotus philippinensis Muell. Arg fruit glandular hairs extract promotes wound healing on different wound model in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Apr 17;15:123. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0647-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 25925413 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Screening and Antiprotozoal Effects of the Methanolic Berberis vulgaris and Acetonic Rhus coriaria Extracts.Molecules. 2020 Jan 27;25(3):550. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030550. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32012795 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and Antioxidant Activities of Rhus coriaria L. (Sumac).Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jan 8;10(1):73. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010073. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33430013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The modern approach to wound treatment].Med Pregl. 2000 Jul-Aug;53(7-8):363-8. Med Pregl. 2000. PMID: 11214479 Review. Croatian.
Cited by
-
Potential anticancer activities of Rhus coriaria (sumac) extract against human cancer cell lines.Biosci Rep. 2021 May 28;41(5):BSR20204384. doi: 10.1042/BSR20204384. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33891003 Free PMC article.
-
MSC Exosomes Containing Valproic Acid Promote Wound Healing by Modulating Inflammation and Angiogenesis.Molecules. 2024 Sep 9;29(17):4281. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174281. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39275128 Free PMC article.
-
By-Products of Agri-Food Industry as Tannin-Rich Sources: A Review of Tannins' Biological Activities and Their Potential for Valorization.Foods. 2021 Jan 11;10(1):137. doi: 10.3390/foods10010137. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33440730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Extraction Methods on the Antioxidant Potential and Cytotoxicity of the Combined Ethanolic Extracts of Daucus carota L., Beta vulgaris L., Phyllanthus emblica L. and Lycopersicon esculentum against Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells.Molecules. 2023 Sep 13;28(18):6589. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186589. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764365 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Quercetin as a Plant-Derived Bioactive Agent in Preventive Medicine and Treatment in Skin Disorders.Molecules. 2024 Jul 5;29(13):3206. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133206. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agra I. K. R., Pires L. L. S., Carvalho P. S. M., Silva-Filho E. A., Smaniotto S., Barreto E. Evaluation of wound healing and antimicrobial properties of aqueous extract from Bowdichia virgilioides stem barks in mice. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 2013;85(3):945–954. doi: 10.1590/S0001-37652013005000049. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mehrabani N. M., Kamalinejad M., Khodaii Z., Kamali J., Hashemi S., Dehghan M. Wound healing effect of aqueous extract of rhus coriaria in rat. Aristotle University Medical Journal. 2017;6(1):p. 5159.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

