Keratinocyte Growth Factor-2 Is Protective in Oleic Acid-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats
- PMID: 31379970
- PMCID: PMC6662415
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9406580
Keratinocyte Growth Factor-2 Is Protective in Oleic Acid-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to examine the role of keratinocyte growth factor-2 (KGF-2) in oleic acid-induced acute lung injury (ALI) in rats.
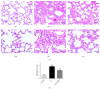
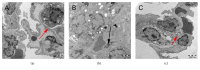
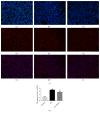
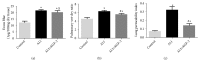
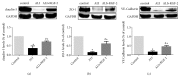
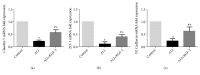
Methods: Forty-five healthy adult male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into 3 groups. Rat ALI model was established by injection of 0.01 mL/kg oleic acid into the tail vein. Rats in the control group were injected with the same amount of normal saline (NS). In the ALI + KGF-2 group, 5 mg/kg of KGF-2 was instilled into the airway of rats 72 hours before the model preparation, and the control group and the ALI model group were instilled with the same amount of NS. The lung permeability index (LPI) and lung wet/dry weight (W / D) ratios were measured 8 hours after the model preparation. The permeability of pulmonary microvascular endothelium was evaluated by Evans blue leakage test. Histopathological changes were observed under light microscope and the ALI pathology score (LIS) was calculated. Ultrastructural changes of lung tissue were observed under electron microscope. The apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay. The expression of Claudin-5, ZO-1, and VE Cadherin in lung tissue was qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by immunohistochemistry, Western Blot, and qRT-PCR, respectively.
Results: The ALI model group had severe lung injury and obvious pathological changes, including alveolar septal thickening and inflammatory cell infiltration. TUNEL assay showed that the apoptosis of ALI group was significantly increased. The LIS score, lung W/D ratio, LPI, and Evans blue leakage were significantly higher than those in the control group; electron microscopy showed that the alveolar-capillary barrier was severely damaged in the ALI group. Compared with the control group, the expression of Claudin-5, ZO-1, and VE cadherin in the lung tissue of the ALI model group was significantly attenuated. After pretreatment with KGF-2, the degree of lung tissue damage was significantly reduced and the pathological changes were significantly improved. TUNEL assay showed that the apoptosis of ALI group was decreased. Lung W/D ratio, LPI, and Evans blue leakage decreased; electron microscopy showed that the alveolar-capillary barrier of ALI group recovered significantly. Compared with the ALI model group, the expression of Claudin-5, ZO-1, and VE cadherin in the lung tissue of the KGF-2 pretreatment group increased.
Conclusion: The results indicate that KGF-2 may attenuate oleic acid-induced ALI in rats by maintaining the pulmonary microvascular endothelial barrier, which is an effective ALI preventive measure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Keratinocyte Growth Factor-2 Reduces Inflammatory Response to Acute Lung Injury Induced by Oleic Acid in Rats by Regulating Key Proteins of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jun 20;2020:8350579. doi: 10.1155/2020/8350579. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32655669 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of keratinocyte growth factor-2 on expressions of chemokine FKN and tight junction protein claudin-5 in lung of rats with acute lung injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Nov;30(11):1066-1070. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.011.011. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30541647 Chinese.
-
The Protective Effect of Sulodexide on Acute Lung Injury Induced by a Murine Model of Obstructive Jaundice.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Aug 26;2022:8717950. doi: 10.1155/2022/8717950. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9803189. doi: 10.1155/2023/9803189. PMID: 36060145 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
[Effect of human placental mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on pulmonary vascular endothelial permeability and lung injury repair in mice with acute lung injury].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Mar 15;34(3):387-392. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201909070. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32174088 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury by up-regulating cellular tight junction protein Claudin-18 expression].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Apr;36(4):377-380. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231204-01036. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38813631 Chinese.
Cited by
-
New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors.WIREs Mech Dis. 2022 Jul;14(4):e1549. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1549. Epub 2022 Feb 9. WIREs Mech Dis. 2022. PMID: 35142107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative study of adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells with rapamycin on paraquat-induced acute lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse model: histological and biochemical study.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 15;16(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04498-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40665395 Free PMC article.
-
Keratinocyte Growth Factor-2 Reduces Inflammatory Response to Acute Lung Injury Induced by Oleic Acid in Rats by Regulating Key Proteins of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jun 20;2020:8350579. doi: 10.1155/2020/8350579. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32655669 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in lung regeneration: from bench to bedside.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 4;23(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05954-6. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39905476 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

