CXCL16 Induces the Progression of Pulmonary Fibrosis through Promoting the Phosphorylation of STAT3
- PMID: 31379980
- PMCID: PMC6652085
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2697376
CXCL16 Induces the Progression of Pulmonary Fibrosis through Promoting the Phosphorylation of STAT3
Abstract
Aim: The transmembrane chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16 (CXCL16) plays a vital role in the pathogenesis of organ fibrosis, including the liver and kidney. However, the detailed biological function of CXCL16 is still not fully understood in the progression of pulmonary fibrosis (PF). The aim of present study is to examine the function of CXCL16 in PF.
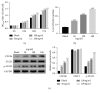
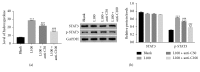
Materials and methods: In this study, we constructed the PF model on mouse by using bleomycin and analyzed the effect of the mouse recombinant protein CXCL16 on mouse lung fibroblast L929 (LF) as well. To further examine the connection between CXCL16 and STAT3 in mouse LF cells, the STAT3 inhibitor AG490 was utilized to inhibit the expression of STAT3. Meanwhile, lipopolysaccharide was used to enhance the phosphorylation of STAT3 (p-STAT3) in mouse LF cells.
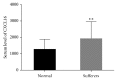
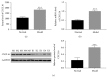
Results: Our results indicated that the level of CXCL16/CXCR6 was significantly upregulated in the mouse PF model. Moreover, the level of p-STAT3 was also promoted. In addition, the mouse recombinant protein CXCL16 not only contributed to the proliferation of mouse LF cells but also induced the expression of p-STAT3 in LF cells. However, the effect of CXCL16 was deeply abolished by the STAT3 inhibitor AG490 in LF cells. Meanwhile, the antibody of CXCL16 deeply reduced the phosphorylation of STAT3 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) cultured cells.
Conclusions: All these results demonstrated that CXCL16 promoted the phosphorylation of STAT3 and further demonstrated that STAT3 was a critical component in CXCL16/CXCR6 signaling pathway. This research not only enhanced the comprehension of CXCL16 but also indicated its potential value as a target in the treatment for human PF.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

