Phosphatidylcholine Extends Lifespan via DAF-16 and Reduces Amyloid-Beta-Induced Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 31379987
- PMCID: PMC6657616
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2860642
Phosphatidylcholine Extends Lifespan via DAF-16 and Reduces Amyloid-Beta-Induced Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
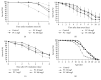
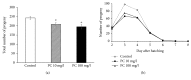
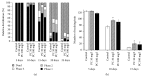
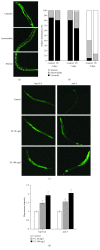
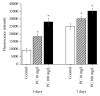
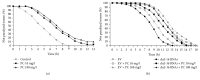
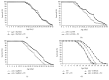
Phosphatidylcholine is one of the major phospholipids comprising cellular membrane and is known to have several health-promoting activities, including the improvement of brain function and liver repair. In this paper, we examine the in vivo effect of dietary supplementation with phosphatidylcholine on the response to environmental stressors and aging in C. elegans. Treatment with phosphatidylcholine significantly increased the survival of worms under oxidative stress conditions. However, there was no significant difference in response to stresses caused by heat shock or ultraviolet irradiation. Oxidative stress is believed to be one of the major causal factors of aging. Then, we examined the effect of phosphatidylcholine on lifespan and age-related physiological changes. Phosphatidylcholine showed a lifespan-extending effect and a reduction in fertility, possibly as a tradeoff for long lifespan. Age-related decline of motility was also significantly delayed by supplementation with phosphatidylcholine. Interestingly, the expressions of well-known longevity-assuring genes, hsp-16.2 and sod-3, were significantly upregulated by dietary intervention with phosphatidylcholine. DAF-16, a transcription factor modulating stress response genes, was accumulated in the nucleus by phosphatidylcholine treatment. Increase of the ROS level with phosphatidylcholine suggests that the antioxidant and lifespan-extending effects are due to the hormetic effect of phosphatidylcholine. Phosphatidylcholine also showed a protective effect against amyloid beta-induced toxicity in Alzheimer's disease model animals. Experiments with long-lived mutants revealed that the lifespan-extending effect of phosphatidylcholine specifically overlapped with that of reduced insulin/IGF-1-like signaling and required DAF-16. These findings showed the antioxidant and antiaging activities of phosphatidylcholine for the first time in vivo. Further studies focusing on the identification of underlying cellular mechanisms involved in the antiaging effect will increase the possibility of using phosphatidylcholine for the development of antiaging therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylserine modulates response to oxidative stress through hormesis and increases lifespan via DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans.Biogerontology. 2020 Apr;21(2):231-244. doi: 10.1007/s10522-020-09856-0. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Biogerontology. 2020. PMID: 31915963
-
Monascin from Monascus-Fermented Products Reduces Oxidative Stress and Amyloid-β Toxicity via DAF-16/FOXO in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Sep 28;64(38):7114-20. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02779. Epub 2016 Sep 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27554775
-
Emodin extends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans through insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway depending on DAF-16 and SIR-2.1.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017 Oct;81(10):1908-1916. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2017.1365592. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28831863
-
DAF-16 target identification in C. elegans: past, present and future.Biogerontology. 2015 Apr;16(2):221-34. doi: 10.1007/s10522-014-9527-y. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Biogerontology. 2015. PMID: 25156270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies of Caenorhabditis elegans DAF-2/insulin signaling reveal targets for pharmacological manipulation of lifespan.Aging Cell. 2006 Feb;5(1):31-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00188.x. Aging Cell. 2006. PMID: 16441841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lung Lipidomic Alterations in Beagle Dogs Infected with Toxocara canis.Animals (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;12(22):3080. doi: 10.3390/ani12223080. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428308 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omic Analysis Reveals Different Effects of Sulforaphane on the Microbiome and Metabolome in Old Compared to Young Mice.Microorganisms. 2020 Sep 29;8(10):1500. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8101500. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33003447 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthoxyline prevents aging and neuronal damage by activating autophagy and DAF-16 expression in Caenorhabditis elegans.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025 Aug 22;29(1):544-555. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2025.2549756. eCollection 2025. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 40861022 Free PMC article.
-
Stress Buffering and Longevity Effects of Amber Extract on Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans).Molecules. 2022 Jun 16;27(12):3858. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123858. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744983 Free PMC article.
-
Serum unsaturated phosphatidylcholines predict longitudinal basal forebrain degeneration in Alzheimer's disease.Brain Commun. 2022 Dec 2;4(6):fcac318. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac318. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 37064049 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

