The Ameliorative Effects of the Ethyl Acetate Extract of Salicornia europaea L. and Its Bioactive Candidate, Irilin B, on LPS-Induced Microglial Inflammation and MPTP-Intoxicated PD-Like Mouse Model
- PMID: 31379989
- PMCID: PMC6652089
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/6764756
The Ameliorative Effects of the Ethyl Acetate Extract of Salicornia europaea L. and Its Bioactive Candidate, Irilin B, on LPS-Induced Microglial Inflammation and MPTP-Intoxicated PD-Like Mouse Model
Abstract
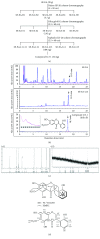
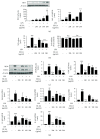
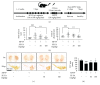
Hyperactivation of microglia, the resident innate immune cells of the central nervous system, exacerbates various neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's disease (PD). Parkinson's disease is generally characterized by a severe loss of dopaminergic neurons in the nigrostriatal pathway, with substantial neuroinflammation and motor deficits. This was experimentally replicated in animal models, using neurotoxins, i.e., LPS (lipopolysaccharides) and MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine). Salicornia europaea L. (SE) has been used as a dietary supplement in Korea and Europe for several years, due to its nutritional and therapeutic value. In this study, we intend to investigate the antineuroinflammatory and anti-PD-like effects of the bioactive fraction/candidate of the SE extract. Initially, we screened various fractions of SE extract using an in vitro antioxidant assay. The optimal fraction was investigated for its in vitro antineuroinflammatory potential in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells and in vivo anti-PD-like potential in MPTP-intoxicated mice. Subsequently, to identify the potential candidate responsible for the elite therapeutic potential of the optimal fraction, we conducted antioxidant activity-guided isolation and purification; the bioactive candidate was structurally characterized using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and chromatographic techniques and further investigated for its in vitro antioxidative and antineuroinflammatory potential. The results of our study indicate that SE-EA and its bioactive candidate, Irilin B, effectively alleviate the deleterious effect of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and promote antioxidative effects. Thus, they exhibit potential as therapeutic candidates against neuroinflammatory and oxidative stress-mediated PD-like neurodegenerative complications.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemical Structure and Biological Activities of Secondary Metabolites from Salicornia europaea L.Molecules. 2021 Apr 13;26(8):2252. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082252. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33924656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attenuation of neuroinflammatory responses and behavioral deficits by Ligusticum officinale (Makino) Kitag in stimulated microglia and MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Apr 22;164:388-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.11.004. Epub 2014 Nov 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25449453
-
α-Asarone attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation by inhibiting NF kappa B activation and mitigates MPTP-induced behavioral deficits in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Oct;97:46-57. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.04.037. Epub 2015 May 15. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25983275
-
Acorus gramineus inhibits microglia mediated neuroinflammation and prevents neurotoxicity in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Dec 18;144(3):506-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.09.026. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23085397
-
Partial depletion and repopulation of microglia have different effects in the acute MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Cell Prolif. 2021 Aug;54(8):e13094. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13094. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 34312932 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Salicornia-Based Skin Cream Application on Healthy Humans' Experimental Model of Pain and Itching.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 26;15(2):150. doi: 10.3390/ph15020150. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215262 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Structure and Biological Activities of Secondary Metabolites from Salicornia europaea L.Molecules. 2021 Apr 13;26(8):2252. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082252. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33924656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calystegia soldanella Extract Exerts Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects via the Regulation of the NF-κB/Nrf-2 Pathways in Mouse Macrophages.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 18;10(10):1639. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101639. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679773 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Polysaccharides in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 4;14:917629. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.917629. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35860666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Clinical Impact of a Polyphenol-Rich Extract from Salicornia ramosissima on Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack and Minor Stroke.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 13;16(24):4307. doi: 10.3390/nu16244307. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39770931 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

