Prolonged Serum Alanine Aminotransferase Elevation Associated with Isotretinoin Administration
- PMID: 31380129
- PMCID: PMC6662412
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9270827
Prolonged Serum Alanine Aminotransferase Elevation Associated with Isotretinoin Administration
Abstract
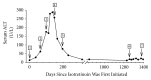
Isotretinoin is a highly effective oral retinoid derivative for severe forms of acne. Despite its high margin of safety, isotretinoin carries a risk of teratogenicity and mild to massive elevations of serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels, as well as infrequent transaminitis. Liver dysfunction induced by isotretinoin is rare but it poses a management dilemma. We describe a 16-year-old male in whom alanine aminotransferase (ALT) rose from a baseline of 13 to 288 U/L after 20 weeks of treatment with 1.0-1.4 mg/kg of oral isotretinoin daily. Though the patient remained asymptomatic, ALT levels did not return to normal limits for approximately 8 months after discontinuation of therapy, an observation that has not been documented in the literature. When oral isotretinoin was readministered for intractable facial acne 3 years later, liver enzymes remained normal throughout the course of therapy. Although the pathogenesis and prognosis of retinoid-induced hepatotoxicity are unknown, this case illustrates that isotretinoin may be safely readministered after normalization of liver function tests.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laboratory Abnormalities in Acne Patients Treated With Oral Isotretinoin: A Retrospective Epidemiological Study.Cureus. 2021 Oct 25;13(10):e19031. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19031. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34853752 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of clinical efficacy, side effects, and laboratory changes among patients with acne vulgaris receiving single versus twice daily dose of oral isotretinoin.Dermatol Ther. 2015 May-Jun;28(3):151-7. doi: 10.1111/dth.12213. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Dermatol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25754162 Clinical Trial.
-
Isotretinoin Use and Liver Enzymes Changes: A Single-Center Study in Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2023 Dec 29;15(12):e51263. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51263. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38161524 Free PMC article.
-
Facial edema induced by isotretinoin use: a case and a review of the side effects of isotretinoin.J Drugs Dermatol. 2006 May;5(5):467-8. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 16703787 Review.
-
Isotretinoin: new therapy for severe acne.Clin Pharm. 1983 Jan-Feb;2(1):12-9. Clin Pharm. 1983. PMID: 6192964 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Isotretinoin on Blood Lipids and Liver Enzymes: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Saudi Arabia.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2024 Sep 4;20:567-575. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S466113. eCollection 2024. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2024. PMID: 39253030 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Evening Primrose Oil Supplementation on Biochemical Parameters and Nutrition of Patients Treated with Isotretinoin for Acne Vulgaris: A Randomized Double-Blind Trial.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 23;14(7):1342. doi: 10.3390/nu14071342. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35405955 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Optimal laboratory testing protocol for patients with acne taking oral isotretinoin.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Apr 16;11(11):2435-2442. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2435. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37123305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kizilyel O., Metin M. S., Elmas Ö. F., Çayir Y., Aktas A. Effects of oral isotretinoin on lipids and liver enzymes in acne patients. Cutis; Cutaneous Medicine for the Practitioner. 2014;94(5):234–238. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

