Correlations Study Between 18F-FDG PET/CT Metabolic Parameters Predicting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation Status and Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31380265
- PMCID: PMC6657738
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00589
Correlations Study Between 18F-FDG PET/CT Metabolic Parameters Predicting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation Status and Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
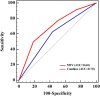
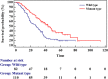
Purpose: This study assessed the ability of metabolic parameters from 18Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) and clinicopathological data to predict epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression/mutation status in patients with lung adenocarcinoma and to develop a prognostic model based on differences in EGFR expression status, to enable individualized targeted molecular therapy. Patients and Methods: Metabolic parameters and clinicopathological data from 200 patients diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma between July 2009 and November 2016, who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT and EGFR mutation testing, were retrospectively evaluated. Multivariate logistic regression was applied to significant variables to establish a prediction model for EGFR mutation status. Overall survival for both mutant and wild-type EGFR was analyzed to establish a multifactor Cox regression model. Results: Of the 200 patients, 115 (58%) exhibited EGFR mutations and 85 (42%) were wild-type. Among selected metabolic parameters, metabolic tumor volume (MTV) demonstrated a significant difference between wild-type and mutant EGFR mutation status, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.60, which increased to 0.70 after clinical data (smoking status) were combined. Survival analysis of wild-type and mutant EGFR yielded mean survival times of 34.451 (95% CI 28.654-40.249) and 53.714 (95% CI 44.331-63.098) months, respectively. Multivariate Cox regression revealed that mutation type, tumor stage, and thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) expression status were the main factors influencing patient prognosis. The hazard ratio for mutant EGFR was 0.511 (95% CI 0.303-0.862) times that of wild-type, and the risk of death was lower for mutant EGFR than for wild-type. The risk of death was lower in TTF-1-positive than in TTF-1-negative patients. Conclusion: 18F-FDG PET/CT metabolic parameters combined with clinicopathological data demonstrated moderate diagnostic efficacy in predicting EGFR mutation status and were associated with prognosis in mutant and wild-type EGFR non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), thus providing a reference for individualized targeted molecular therapy.
Keywords: EGFR; PET/CT; lung adenocarcinoma; metabolic parameters; prognosis.
Figures
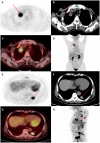
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

