The interaction between RUNX2 and core binding factor beta as a potential therapeutic target in canine osteosarcoma
- PMID: 31381810
- PMCID: PMC7233265
- DOI: 10.1111/vco.12526
The interaction between RUNX2 and core binding factor beta as a potential therapeutic target in canine osteosarcoma
Abstract
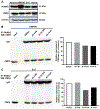
Osteosarcoma remains the most common primary bone tumour in dogs with half of affected dogs unable to survive 1 year beyond diagnosis. New therapeutic options are needed to improve outcomes for this disease. Recent investigations into potential therapeutic targets have focused on cell surface molecules with little clear therapeutic benefit. Transcription factors and protein interactions represent underdeveloped areas of therapeutic drug development. We have utilized allosteric inhibitors of the core binding factor transcriptional complex, comprised of core binding factor beta (CBFβ) and RUNX2, in four canine osteosarcoma cell lines Active inhibitor compounds demonstrate anti-tumour activities with concentrations demonstrated to be achievable in vivo while an inactive, structural analogue has no activity. We show that CBFβ inhibitors are capable of inducing apoptosis, inhibiting clonogenic cell growth, altering cell cycle progression and impeding migration and invasion in a cell line-dependent manner. These effects coincide with a reduced interaction between RUNX2 and CBFβ and alterations in expression of RUNX2 target genes. We also show that addition of CBFβ inhibitors to the commonly used cytotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs doxorubicin and carboplatin leads to additive and/or synergistic anti-proliferative effects in canine osteosarcoma cell lines. Taken together, we have identified the interaction between components of the core binding factor transcriptional complex, RUNX2 and CBFβ, as a potential novel therapeutic target in canine osteosarcoma and provide justification for further investigations into the anti-tumour activities we describe here.
Keywords: RUNX2; canine sarcoma; core-binding factor beta; novel therapeutic targets; osteosarcoma; transcription factor.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Vos HI, Coenen MJ, Guchelaar HJ, et al. The role of pharmacogenetics in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Drug Discov Today 2016;21:1775–1786. - PubMed
-
- Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, et al. Current and future therapeutic approaches for osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2018;18:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Maniscalco L Canine osteosarcoma: understanding its variability to improve treatment. Vet J 2015;203:135–136. - PubMed
-
- Kansara M, Teng MW, Smyth MJ, et al. Translational biology of osteosarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer 2014;14:722–735. - PubMed

