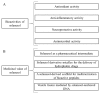
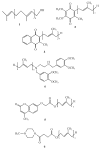
Bioactivities and Medicinal Value of Solanesol and Its Accumulation, Extraction Technology, and Determination Methods
- PMID: 31382471
- PMCID: PMC6722674
- DOI: 10.3390/biom9080334
Bioactivities and Medicinal Value of Solanesol and Its Accumulation, Extraction Technology, and Determination Methods
Abstract
Solanesol, an aliphatic terpene alcohol composed of nine isoprene units, is mainly found in solanaceous plants. Particularly, tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), belonging to the Solanaceae family, is the richest plant source of solanesol, and its leaves have been regarded as the ideal material for solanesol extraction. Since the discovery of solanesol in tobacco, significant progress has been achieved in research on solanesol's bioactivities, medicinal value, accumulation, extraction technology, and determination methods. Solanesol possesses strong free radical absorption ability and antioxidant activity owing to the presence of several non-conjugated double bonds. Notably, solanesol's anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and antimicrobial activities have been previously demonstrated. Solanesol is a key intermediate in the synthesis of coenzyme Q10, vitamin K2, and the anticancer agent synergiser N-solanesyl-N,N'-bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl) ethylenediamine. Other applications of solanesol include solanesol derivative micelles for hydrophobic drug delivery, solanesol-derived scaffolds for bioactive peptide multimerization, and solanesol-anchored DNA for mediating vesicle fusion. Solanesol accumulation in plants is influenced by genetic and environmental factors, including biotic stresses caused by pathogen infections, temperature, illumination, and agronomic measures. Seven extraction technologies and seven determination methods of solanesol are also systematically summarized in the present review. This review can serve as a reference for solanesol's comprehensive application.
Keywords: accumulation; bioactivity; determination methods; extraction technology; medicinal value; solanesol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Solanesol Biosynthesis in Plants.Molecules. 2017 Mar 23;22(4):510. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040510. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28333111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Sequencing Provides Insights into the Regulation of Solanesol Biosynthesis in Nicotiana tabacum Induced by Moderately High Temperature.Biomolecules. 2018 Dec 7;8(4):165. doi: 10.3390/biom8040165. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30544626 Free PMC article.
-
Organ- and Growing Stage-Specific Expression of Solanesol Biosynthesis Genes in Nicotiana tabacum Reveals Their Association with Solanesol Content.Molecules. 2016 Nov 15;21(11):1536. doi: 10.3390/molecules21111536. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27854285 Free PMC article.
-
[Determination of solanesol in the extracts of tobacco leaves by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)].Se Pu. 1997 Nov;15(6):544-5. Se Pu. 1997. PMID: 15739347 Chinese.
-
Solanesol: added value from Solanaceous waste.Phytochemistry. 2011 Aug;72(11-12):1323-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.03.015. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Phytochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21459392 Review.
Cited by
-
Coenzyme Q10: Novel Formulations and Medical Trends.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 10;21(22):8432. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228432. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33182646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemicals derived from Nicotiana tabacum L. plant contribute to pharmaceutical development.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 12;15:1372456. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1372456. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38681197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anxiolytic Effect of Two Tobacco Essential Oils (Nicotiana tabacum Linn.) on Mice.Molecules. 2021 Jul 9;26(14):4171. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144171. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299447 Free PMC article.
-
Solanesol: a promising natural product.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 24;16:1504245. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1504245. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40196358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Barleria longiflora L. f. From Siriya Kalvarayan Hills.Scientifica (Cairo). 2025 May 28;2025:8055358. doi: 10.1155/sci5/8055358. eCollection 2025. Scientifica (Cairo). 2025. PMID: 40475056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yan N., Liu Y., Gong D., Du Y., Zhang H., Zhang Z. Solanesol: A review of its resources, derivatives, bioactivities, medicinal applications, and biosynthesis. Phytochem. Rev. 2015;14:403–417. doi: 10.1007/s11101-015-9393-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous