MiT Family Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma: from the Early Descriptions to the Current Knowledge
- PMID: 31382581
- PMCID: PMC6721505
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11081110
MiT Family Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma: from the Early Descriptions to the Current Knowledge
Abstract
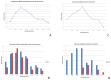
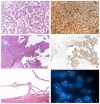
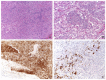
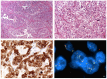
The new category of MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma has been included into the World Health Organization (WHO) classification in 2016. The MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma comprises Xp11 translocation renal cell carcinoma harboring TFE3 gene fusions and t(6;11) renal cell carcinoma harboring TFEB gene fusion. At the beginning, they were recognized in childhood; nevertheless, it has been demonstrated that these neoplasms can occur in adults as well. In the nineties, among Xp11 renal cell carcinoma, ASPL, PRCC, and SFPQ (PSF) were the first genes recognized as partners in TFE3 rearrangement. Recently, many other genes have been identified, and a wide spectrum of morphologies has been described. For this reason, the diagnosis may be challenging based on the histology, and the differential diagnosis includes the most common renal cell neoplasms and pure epithelioid PEComa/epithelioid angiomyolipoma of the kidney. During the last decades, many efforts have been made to identify immunohistochemical markers to reach the right diagnosis. To date, staining for PAX8, cathepsin K, and melanogenesis markers are the most useful identifiers. However, the diagnosis requires the demonstration of the chromosomal rearrangement, and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) is considered the gold standard. The outcome of Xp11 translocation renal cell carcinoma is highly variable, with some patients surviving decades with indolent disease and others dying rapidly of progressive disease. Despite most instances of t(6;11) renal cell carcinoma having an indolent clinical course, a few published cases demonstrate aggressive behavior. Recently, renal cell carcinomas with TFEB amplification have been described in connection with t(6;11) renal cell carcinoma. Those tumors appear to be associated with a more aggressive clinical course. For the aggressive cases of MiT family translocation carcinoma, the optimal therapy remains to be determined; however, new target therapies seem to be promising, and the search for predictive markers is mandatory.
Keywords: 11) translocation renal cell carcinoma; FISH; MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma; TFE3; TFEB; TFEB-amplified renal cell carcinoma; Xp11 translocation renal cell carcinoma; t(6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Xia Q.Y., Wang X.T., Ye S.B., Wang X., Li R., Shi S.S., Fang R., Zhang R.S., Ma H.H., Lu Z.F., et al. Novel gene fusion of PRCC-MITF defines a new member of MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis and detection of the gene fusion by RNA sequencing and FISH. Histopathology. 2018;72:786–794. doi: 10.1111/his.13439. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xia Q.Y., Wang X.T., Zhan X.M., Tan X., Chen H., Liu Y., Shi S.S., Wang X., Wei X., Ye S.B., et al. Xp11 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinomas (RCCs) With RBM10-TFE3 Gene Fusion Demonstrating Melanotic Features and Overlapping Morphology With t(6;11) RCC: Interest and Diagnostic Pitfall in Detecting a Paracentric Inversion of TFE3. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017;41:663–676. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000837. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xia Q.Y., Wang Z., Chen N., Gan H.L., Teng X.D., Shi S.S., Wang X., Wei X., Ye S.B., Li R., et al. Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma with NONO-TFE3 gene fusion: Morphology, prognosis, and potential pitfall in detecting TFE3 gene rearrangement. Mod. Pathol. 2017;30:416–426. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2016.204. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang X.T., Xia Q.Y., Ni H., Ye S.B., Li R., Wang X., Shi S.S., Zhou X.J., Rao Q. SFPQ/PSF-TFE3 renal cell carcinoma: A clinicopathologic study emphasizing extended morphology and reviewing the differences between SFPQ-TFE3 RCC and the corresponding mesenchymal neoplasm despite an identical gene fusion. Hum. Pathol. 2017;63:190–200. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.02.022. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

