Hybrid sequencing of the Gynostemma pentaphyllum transcriptome provides new insights into gypenoside biosynthesis
- PMID: 31382891
- PMCID: PMC6683540
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-019-6000-y
Hybrid sequencing of the Gynostemma pentaphyllum transcriptome provides new insights into gypenoside biosynthesis
Abstract
Background: Gypenosides are a group of triterpene saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum that are the same as or very similar to ginsenosides from the Panax species. Several enzymes involved in ginsenoside biosynthesis have been characterized, which provide important clues for elucidating the gypenoside biosynthetic pathway. We suppose that gypenosides and ginsenosides may have a similar biosynthetic mechanism and that the corresponding enzymes in the two pathways may have considerable similarity in their sequences. To further understand gypenoside biosynthesis, we sequenced the G. pentaphyllum transcriptome with a hybrid sequencing-based strategy and then determined the candidate genes involved in this pathway using phylogenetic tree construction and gene expression analysis.
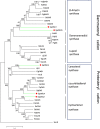
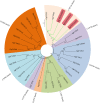
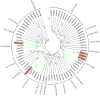
Results: Following the PacBio standard analysis pipeline, 66,046 polished consensus sequences were obtained, while Illumina data were assembled into 140,601 unigenes with Trinity software. Then, these output sequences from the two analytical routes were merged. After removing redundant data with CD-HIT software, a total of 140,157 final unigenes were obtained. After functional annotation, five 2,3-oxidosqualene cyclase genes, 145 cytochrome P450 genes and 254 UDP-glycosyltransferase genes were selected for the screening of genes involved in gypenoside biosynthesis. Using phylogenetic analysis, several genes were divided into the same subfamilies or closely related evolutionary branches with characterized enzymes involved in ginsenoside biosynthesis. Using real-time PCR technology, their expression patterns were investigated in different tissues and at different times after methyl jasmonate induction. Since the genes in the same biosynthetic pathway are generally coexpressed, we speculated that GpOSC1, GpCYP89, and GpUGT35 were the leading candidates for gypenoside biosynthesis. In addition, six GpWRKYs and one GpbHLH might play a possible role in regulating gypenoside biosynthesis.
Conclusions: We developed a hybrid sequencing strategy to obtain longer length transcriptomes with increased accuracy, which will greatly contribute to downstream gene screening and characterization, thus improving our ability to elucidate secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways. With this strategy, we found several candidate genes that may be involved in gypenoside biosynthesis, which laid an important foundation for the elucidation of this biosynthetic pathway, thus greatly contributing to further research in metabolic regulation, synthetic biology and molecular breeding in this species.
Keywords: Biosynthesis; Gynostemma pentaphyllum; Gypenosides; Iso-Seq; Transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcriptome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factor gene family involved in the regulation of gypenoside biosynthesis in Gynostemma pentaphyllum.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2020 Sep;154:238-247. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.05.040. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32563852
-
Gene excavation and expression analysis of CYP and UGT related to the post modifying stage of gypenoside biosynthesis in Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino by comprehensive analysis of RNA and proteome sequencing.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 7;16(12):e0260027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260027. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34874937 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide characterization of the bHLH gene family in Gynostemma pentaphyllum reveals its potential role in the regulation of gypenoside biosynthesis.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Mar 20;24(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04879-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38509465 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of Gypenosides: A review on preclinical studies in neuropsychiatric disorders.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 5;978:176766. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176766. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38908668 Review.
-
Progress on the Studies of the Key Enzymes of Ginsenoside Biosynthesis.Molecules. 2018 Mar 6;23(3):589. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030589. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29509695 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis and Identification of Dammarenediol-II Synthase Involved in Saponin Biosynthesis in Gynostemma longipes.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 25;13:852377. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.852377. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35401630 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of OSC Gene Family in Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Cucurbitaceae).Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 4;14(12):1599. doi: 10.3390/life14121599. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768308 Free PMC article.
-
De novo sequencing of Bletilla striata (Orchidaceae) transcriptome and identification of genes involved in polysaccharide biosynthesis.Genet Mol Biol. 2020 Jun 26;43(3):e20190417. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0417. eCollection 2020. Genet Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32609279 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveals the accumulation patterns of key metabolites associated with flavonoids and terpenoids of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 15;14(1):8644. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57716-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38622163 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights into the Molecular Mechanism Underlying the Effect of MeJA Treatment on the Biosynthesis of Saikosaponins in Bupleurum chinense DC.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;13(2):563. doi: 10.3390/life13020563. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gao XF, Chen SK, Gu ZJ, Zhao JZ. A chromosomal study on the genus Gynostemma (Cucurbitaceae). Acta Bot Yunnanica. 1995;17(3):312-16.
-
- Chen SK. A classificatory system and geographical distribution of the genus Gynostemma Bl. (Cucurbitaceae) Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica. 1995;33:403–410.
-
- Razmovski-Naumovski V, Huang HW, Tran VH, Li GQ, Duke CC, Roufogalis BD. Chemistry and pharmacology of Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Phytochem Rev. 2005;4(2–3):197–219.
-
- Kim JH, Han YN. Dammarane-type saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Phytochemistry. 2011;72(11–12):1453–1459. - PubMed
-
- Ky PT, Huong PT, My TK, Anh PT, Kiem PV, Minh CV, Cuong NX, Thao NP, Nhiem NX, Hyun JH, et al. Dammarane-type saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Phytochemistry. 2010;71(8–9):994–1001. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

