A regional audit system for stillbirth: a way to better understand the phenomenon
- PMID: 31382995
- PMCID: PMC6683556
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-019-2432-2
A regional audit system for stillbirth: a way to better understand the phenomenon
Abstract
Background: Implementation of high-quality national audits for perinatal mortality are needed to improve the registration of all perinatal deaths and the identification of the causes of death. This study aims to evaluate the implementation of a Regional Audit System for Stillbirth in Emilia-Romagna Region, Italy.
Methods: For each stillbirth (≥ 22 weeks of gestation, ≥ 500 g) occurred between January 1, 2014 to December 1, 2016 (n = 332), the same diagnostic workup was performed and a clinical record with data about mother and stillborn was completed. Every case was discussed in a multidisciplinary local audit to assess both the cause of death (ReCoDe classification) and the quality of care. Data were reviewed by the Regional Audit Group. Stillbirth rates, causes of death and the quality of care were established for each case.
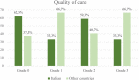
Results: Total stillbirth rate was 3.09 per 1000 births (332/107,528). Late stillbirth rate was 2.3 per 1000 (251/107,087). Sixteen stillbirths were not registered by the Regional Birth Register. The most prevalent cause of death was placental disorder (33.3%), followed by fetal (17.6%), cord (14.2%) and maternal disorders (7.6%). Unexplained cases were 14%. Compared to local audits, the regional group attributed different causes of death in 17% of cases. At multivariate analysis, infections were associated with early stillbirths (OR 3.38, CI95% 1.62-7.03) and intrapartum cases (OR 6.64, CI95% 2.61-17.02). Placental disorders were related to growth restriction (OR 1.89, CI95% 1.06-3.36) and were more frequent before term (OR 1.86, CI95% 1.11-3.15). Stillbirths judged possibly/probably preventable with a different management (10.9%) occurred more frequently in non-Italian women and were mainly related to maternal disorders (OR 6.64, CI95% 2.61-17.02).
Conclusions: Regional Audit System for Stillbirth improves the registration of stillbirth and allows to define the causes of death. Moreover, sub-optimal care was recognized, allowing to identify populations which could benefit from preventive measures.
Keywords: Causes of death; Perinatal audit; Quality of care; Stillbirth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lawn JE, Blencowe H, Waiswa P, et al. For The Lancet ending preventable stillbirths series study group with The Lancet stillbirth epidemiology investigator group. Stillbirths: rates, risk factors, and acceleration towards 2030. Lancet. 2016;387(10018):587–603. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00837-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- You D, Hug L, Ejdemyr S, et al. Global, regional, and national levels and trends in under-5 mortality between 1990 and 2015, with scenario-based projections to 2030: a systematic analysis by the UN inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. Lancet. 2015;386(10010):2275–2286. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00120-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Flenady V, Wojcieszek AM, Middleton P, et al. For the lancet ending preventable stillbirths study group and the lancet stillbirths in high-income countries Investigator Group. Stillbirths: recall to action in high-income countries. Lancet. 2016;387(10019):691–702. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01020-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Every newborn: an action plan to end preventable deaths. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical