Targeting CDK9 and MCL-1 by a new CDK9/p-TEFb inhibitor with and without 5-fluorouracil in esophageal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31384313
- PMCID: PMC6659187
- DOI: 10.1177/1758835919864850
Targeting CDK9 and MCL-1 by a new CDK9/p-TEFb inhibitor with and without 5-fluorouracil in esophageal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: CDK9 inhibitors are antitumorigenic against solid tumors, including esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). However, efficacy of a CDK9 inhibitor combined with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and target proteins that are targeted by these agents in EAC are unknown.
Methods: The anti-EAC efficacy of a new CDK9 inhibitor, BAY1143572, with and without 5-FU was assessed in vitro and in xenograft models in athymic nu/nu mice. Synergy between BAY1143572 and 5-FU in inhibiting cell proliferation was analyzed by calculating the combination index using CompuSyn software. Potential targets of BAY1143572 and 5-FU were identified by reverse-phase protein array. The effects of BAY1143572 and 5-FU on MCL-1 in vitro were analyzed by Western blotting, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. MCL-1 protein expression in tumors from patients with locoregional EAC treated with chemoradiation and surgery was assessed by immunohistochemistry.
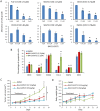
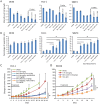
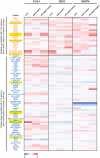
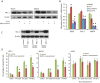
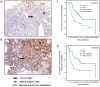
Results: BAY1143572 had dose-dependent antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects and demonstrated synergy with 5-FU against EAC in vitro. The median volumes of FLO-1 and ESO-26 xenografts treated with 5-FU plus BAY114352 were significantly smaller than those of xenografts treated with either agent alone (p < 0.05). BAY1143572 downregulated MCL-1 by inhibiting HIF-1α binding to the MCL-1 promoter. 5-FU enhanced BAY1143572-induced MCL-1 downregulation and stable MCL-1 overexpression reduced the apoptosis induced by BAY1143572 and 5-FU in vitro. High patients' tumor MCL-1 expression was correlated with shorter overall and recurrence-free survival.
Conclusions: BAY1143572 and 5-FU have synergistic antitumorigenic effects against EAC. MCL-1 is a downstream target of CDK9 inhibitors and a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation in EAC.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil and MCL-1; CDK9; adenocarcinoma; esophagus.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 9 by a novel inhibitor enhances radiosensitization and identifies Axl as a novel downstream target in esophageal adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2019 Jul 23;10(45):4703-4718. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27095. eCollection 2019 Jul 23. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31384397 Free PMC article.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(15):iii-ix, xi-162. doi: 10.3310/hta12150. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462574
-
Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 29;8(8):CD004064. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004064.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28850174 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
Mcl-1 expression is a predictive marker of response to gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel for metastatic pancreatic cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 20;14(1):21953. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73020-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39304727 Free PMC article.
-
Leonurine Promotes Cisplatin Sensitivity in Human Cervical Cancer Cells Through Increasing Apoptosis and Inhibiting Drug-Resistant Proteins.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 May 15;14:1885-1895. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S252112. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32523334 Free PMC article.
-
CDK9 inhibitors for the treatment of solid tumors.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;229:116470. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116470. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39127153 Review.
-
CDK9: A Comprehensive Review of Its Biology, and Its Role as a Potential Target for Anti-Cancer Agents.Front Oncol. 2021 May 10;11:678559. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.678559. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34041038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Super-enhancers in esophageal carcinoma: Transcriptional addictions and therapeutic strategies.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 27;12:1036648. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1036648. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ychou M, Boige V, Pignon JP, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: an FNCLCC and FFCD multicenter phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1715–1721. - PubMed
-
- van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ, et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 2074–2084. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro J, van Lanschot JJ, Hulshof MC, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16: 1090–1098. - PubMed
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010; 376: 687–697. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

