Myocardial contractile dispersion: A new marker for the severity of cirrhosis?
- PMID: 31384410
- PMCID: PMC6669422
- DOI: 10.15171/jcvtr.2019.25
Myocardial contractile dispersion: A new marker for the severity of cirrhosis?
Abstract
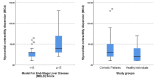
Introduction: Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy (CCM) develops in about half of all cirrhotic patients, affecting the long-term morbidity and mortality. Although some studies have shown an increased QT-interval in cirrhotic patients, no evidences of myocardial contractile and QT dispersion (QTd) changes are available. This study aimed to compare myocardial contractile dispersion (MCd), using tissue Doppler imaging (TDI), as well as QTd between cirrhotic patients and healthy individuals, investigating their associations with cirrhosis severity. Methods: This prospective cross-sectional study was conducted on patients with confirmed liver cirrhosis and healthy individuals. Participants with structural heart disease, heart ventricular pacing, electrolyte abnormalities, using drugs affecting QT interval were excluded. All individuals underwent 2D echocardiography, and TDI by vivid E9 echo machine. MCd and QTd were considered as main outcomes. Chi-square, independent-sample t test, and Pearson correlation test, were used for statistical analyses by SPPS version 17.0. P value <0:05 was considered statistically significant. Results: Sixty participants (40 male/20 female) with a mean age of 40.1 ± 7.1 years in two groups of cirrhotic patients (n=30) and healthy individuals (n=30) were studied. Both groups were statistically similar in terms of age (P = 0.31) and gender (P = 0.39). MCd and QTd of cirrhotic patients were significantly higher than healthy individuals (MCd: 41.0 ± 26.8 versus 27.6±18.1; P = 0.028; and QTd: 37.0 ± 22.1 versus 25.3 ± 8.9; P = 0.010). Cirrhotic patients with MELD score <15 had a lower MCd in comparison to score ≥15 (29.2 ± 13.8 versus 50.0 ± 31.1, P = 0.034). Conclusion: Cirrhosis was associated with increased MCd, assessed by TDI. Also, MCd and QTd were associated with a higher MELD score. According to the results, it seems that MCd and QTd might be useful predictor of ventricular arrhythmia and negative prognostic factor in cirrhotic patients.
Keywords: Cirrhotic Cardiomyopathy; Myocardial Contractile Dispersion; QT Dispersion; Tissue Doppler Imaging.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources