Relationship between Anatomical Variations of Sinonasal Area and Maxillary Sinus Pneumatization
- PMID: 31384589
- PMCID: PMC6666940
Relationship between Anatomical Variations of Sinonasal Area and Maxillary Sinus Pneumatization
Abstract
Introduction: Maxillary sinuses are among the largest paranasal sinuses with various shapes and volumes. The dimensions and volumes of maxillary sinuses play an important role in the surgical treatment plan. The higher levels of pneumatization of alveolar bone lead to the increase of odontogenic sinusitis which cause problems in dental implantation. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the relationship between maxillary sinus volume and pneumatization and anatomical factors.
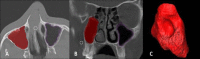
Materials and methods: In this cross-sectional study, computed tomography (CT) images of the healthy maxillary sinuses of 199 adult patients were reviewed. Amira software was used for the measurement of sinus volume. Sinus pneumatization of the alveolar bone in coronal CT scan images in the posterior teeth areas was measured. Moreover, anatomical variations of the sinonasal region, such as nasal septal deviation, and size of the ostium were measured and recorded. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, the t-test, and the Pearson's and Spearman's correlation coefficients were applied for data analysis.
Results: According to the obtained results, the mean value of the maxillary sinus volume and the alveolar bone pneumatization were 15.54 mm3 and 3.54 mm, respectively. The mean value of the maxillary sinus volume was statistically higher among males than females (P<0.001). The prevalence of nasal septal deviation, concha bullosa, and maxillary sinus septa were 14.6%, 14.6% and 6% respectively. There were no association between anatomical factors, including the nasal septal deviation, the size of the ostium, concha bullosa, and maxillary sinus septa and maxillary sinus volume and pneumatization. P-value less than 0.05 was statistically significant.
Conclusion: No correlation was observed between the anatomical variations of the sinonasal region and maxillary sinus volume and pneumatization.
Keywords: Anatomical variations; Computed tomography scan; Maxillary sinus volume; Pneumatization.
Figures
References
-
- Koppe T, Nakatsukasa M, Yamanaka A. Implication of craniofacial morphology for the pneumatization pattern of the human alveolar process. Acta Medica Lituanica. 2005;12(1):40–6.
-
- Rae T, Hill R, Hamada Y, Koppe T. Clinical variation of maxillary sinus volume in Japanese macaques (Macaca fuscata) American journal of primatology. 2003;59(4):153–8. - PubMed
-
- Sharan A, Madjar D. Maxillary sinus Pneumatization following extractions: A Radiographic study. The international J Oral-Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(1):8. - PubMed
-
- Hyun Cho S, Kim T, Kim K, Lee J, Lee D, Kim J. Factors for Maxillary Sinus Volume and Craniofacial Anatomical Features in Adults with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Archives of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery . 2010;136(6):610. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources