Public Health Approaches to Type 2 Diabetes Prevention: the US National Diabetes Prevention Program and Beyond
- PMID: 31385061
- PMCID: PMC6682852
- DOI: 10.1007/s11892-019-1200-z
Public Health Approaches to Type 2 Diabetes Prevention: the US National Diabetes Prevention Program and Beyond
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Public Health Approaches to Type 2 Diabetes Prevention: the US National Diabetes Prevention Program and Beyond.Curr Diab Rep. 2020 Jun 27;20(8):36. doi: 10.1007/s11892-020-01323-x. Curr Diab Rep. 2020. PMID: 32591936 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose of review: This article highlights foundational evidence, translation studies, and current research behind type 2 diabetes prevention efforts worldwide, with focus on high-risk populations, and whole-population approaches as catalysts to global prevention.
Recent findings: Continued focus on the goals of foundational lifestyle change program trials and their global translations, and the targeting of those at highest risk through both in-person and virtual modes of program delivery, is critical. Whole-population approaches (e.g., socioeconomic policies, healthy food promotion, environmental/systems changes) and awareness raising are essential complements to efforts aimed at high-risk populations. Successful type 2 diabetes prevention strategies are being realized in the USA through the National Diabetes Prevention Program and elsewhere in the world. A multi-tiered approach involving appropriate risk targeting and whole-population efforts is essential to curb the global diabetes epidemic.
Keywords: Diabetes policy; Diabetes prevention; Diabetes prevention program; National Diabetes Prevention Program; Obesity; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Stephanie M. Gruss, Kunthea Nhim, Edward Gregg, Miriam Bell, Elizabeth Luman, and Ann Albright declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
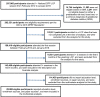
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor Regarding "Public Health Approaches to Type 2 Diabetes Prevention: The US National Diabetes Prevention Program and Beyond".Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Nov 20;19(11):130. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1262-y. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31748826 No abstract available.
References
-
- • International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes atlas 8th edition 2017 global fact sheet. 2017. Available at https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-figures.html. Accessed April 14, 2019. Findings indicate the significant and costly economic and disease burden that diabetes has across the world.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes 2017 report card. 2017. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/library/diabetesreportcard2017-508.pdf. Accessed April 14, 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

