MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging to Investigate Lipid and Bile Acid Modifications Caused by Lentil Extract Used as a Potential Hypocholesterolemic Treatment
- PMID: 31385259
- PMCID: PMC6805814
- DOI: 10.1007/s13361-019-02265-9
MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging to Investigate Lipid and Bile Acid Modifications Caused by Lentil Extract Used as a Potential Hypocholesterolemic Treatment
Abstract
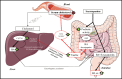
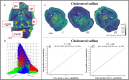
This paper reports matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging to investigate systematic effects of a lentil extract treatment to lower cholesterol levels. For this purpose, mass spectrometry imaging was used to spatially investigate modifications in the lipid composition and cholesterol levels in the brain, liver, and intestines as well as bile acids in the liver and intestine of rats treated with lentil extract. Neither the lipid composition nor cholesterol levels in the brain samples were found to be significantly different between the treated and not-treated animal groups. The hypercholesterolemic livers showed signs of steatosis (lipid marker PG 36:4), but no modifications in bile acid, cholesterol, and lipid composition. We found significant differences (AUC > 0.75) in the intestines regarding bile acid and lipid composition after treatment with the lentil extract. The treated rats showed a decreased reabsorption (increased excretion) of ursodeoxycholic acid, deoxycholic acid, and chenodeoxycholic acid and an increased deconjugation of taurine-conjugated bile acids (taurochenodeoxycholic acid, taurodeoxycholic acid, taurocholic acid, and 3-keto-taurocholic acid). This indicates that the lentil extract lowers the total cholesterol level in two synergic ways: (i) it increases the excretion of bile acids; hence, new bile acids are produced in the liver from serum cholesterol and (ii) the prebiotic effect leads to free taurine which upregulates the de novo synthesis of bile acid from cholesterol while activating LDL receptors. We demonstrate here that mass spectrometry imaging is a valuable tool for a better understanding of the effects of treatments such as for the synergistic cholesterol-lowering effect of the lentil extract.
Keywords: Imaging mass spectrometry; LCMS; Lentils; Lipids; MALDI-MSI; Neutraceutics.
Figures




References
-
- Jimenez-Chillaron JC, Diaz R, Martinez D, Pentinat T, Ramon-Krauel M, Ribo S, Plosch T. The role of nutrition on epigenetic modifications and their implications on health. Biochimie. 2012;94:2242–2263. - PubMed
-
- Kilonzo-Nthenge, A.K, S.N Nahasnon..: Soybean in monogastric nutrition: modifications to add value and disease prevention properties. (2013)
-
- Johnson CR, Thavarajah D, Combs GF, Thavarajah P. Lentil (Lens culinaris L.): a prebiotic-rich whole food legume. Food Res. Int. 2013;51:107–113.
-
- Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V., Cecchini, C., Vila-Donat, P., Caprioli, G., Cifani, C., Coman, M.M., Cresci, A., Fiorini, D., Ricciutelli, M., Silvi, S., Vittori, S., Sagratini, G.: Evaluation of the hypocholesterolemic effect and prebiotic activity of a lentil (Lens culinaris Medik) extract. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 61, (2017) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

