Case-Based Review: meningioma
- PMID: 31386096
- PMCID: PMC6668267
- DOI: 10.1093/nop/npv063
Case-Based Review: meningioma
Abstract
Meningioma is by far the most common primary intracranial tumor in adults. Treatment of meningioma is complex due to a tremendous amount of variability in tumor behavior. Many patients are incidentally found to have tumors that will remain asymptomatic throughout their lives. It is important to identify these patients so that they can be spared from potentially morbid interventions. On the other end of the spectrum, high-grade meningiomas can behave very aggressively. When treatment is necessary, surgical resection is the cornerstone of meningioma therapy. Studies spanning decades have demonstrated that extent of resection correlates with prognosis. Radiation therapy, either in the form of external beam radiation therapy or stereotactic radiosurgery, represents another important therapeutic tool that can be used in place of or as a supplement to surgery. There are no chemotherapeutic agents of proven efficacy against meningioma, and chemotherapy treatment is generally reserved for patients who have exhausted surgical and radiotherapy options. Ongoing and future studies will help to answer unresolved questions such as the optimum use of radiation in resected WHO grade II meningiomas and the efficacy of additional chemotherapy agents.
Keywords: chemotherapy; meningioma; radiation; radiosurgery; surgery.
Figures
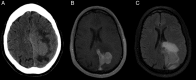
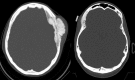
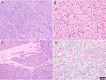
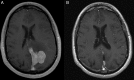
References
-
- Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, et al. Incidental findings on brain MRI in the general population. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(18):1821–1828. - PubMed
-
- Staneczek W, Janisch W. Epidemiologic data on meningiomas in East Germany 1961–1986: incidence, localization, age and sex distribution. Clin Neuropathol. 1992;11(3):135–141. - PubMed
-
- Preston DL, Ron E, Yonehara S, et al. Tumors of the nervous system and pituitary gland associated with atomic bomb radiation exposure. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94(20):1555–1563. - PubMed

