Reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress response induces apoptosis of Mycobacterium avium-infected macrophages by activating regulated IRE1-dependent decay pathway
- PMID: 31386788
- PMCID: PMC6899680
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.13094
Reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress response induces apoptosis of Mycobacterium avium-infected macrophages by activating regulated IRE1-dependent decay pathway
Abstract
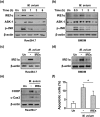
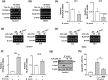
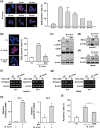
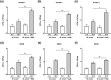
Mycobacterium avium, a slow-growing nontuberculous mycobacterium, causes fever, diarrhoea, loss of appetite, and weight loss in immunocompromised people. We have proposed that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated apoptosis plays a critical role in removing intracellular mycobacteria. In the present study, we investigated the role of the regulated IRE1-dependent decay (RIDD) pathway in macrophages during M. avium infection based on its role in the regulation of gene expression. The inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1)/apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signalling pathway was activated in macrophages after infection with M. avium. The expression of RIDD-associated genes, such as Bloc1s1 and St3gal5, was decreased in M. avium-infected macrophages. Interestingly, M. avium-induced apoptosis was significantly suppressed by pretreatment with irestatin (inhibitor of IRE1α) and 4μ8c (RIDD blocker). Macrophages pretreated with N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) showed decreased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), IRE1α, and apoptosis after M. avium infection. The expression of Bloc1s1 and St3gal5 was increased in NAC-pretreated macrophages following infection with M. avium. Growth of M. avium was significantly increased in irestatin-, 4μ8c-, and NAC-treated macrophages compared with the control. The data indicate that the ROS-mediated ER stress response induces apoptosis of M. avium-infected macrophages by activating IRE1α-RIDD. Thus, activation of IRE1α suppresses the intracellular survival of M. avium in macrophages.
Keywords: ER stress; IRE1α; Mycobacterium avium; RIDD; apoptosis.
© 2019 The Authors. Cellular Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) signaling pathway plays a major role in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013 Nov 2;12:158. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-158. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013. PMID: 24180212 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium bovis Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated-Apoptosis by Activating IRF3 in a Murine Macrophage Cell Line.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Dec 12;6:182. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00182. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 28018864 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium avium MAV2054 protein induces macrophage apoptosis by targeting mitochondria and reduces intracellular bacterial growth.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 30;6:37804. doi: 10.1038/srep37804. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27901051 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Jan.;18(1):1-14. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600043. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28070992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The unknown face of IRE1α - Beyond ER stress.Eur J Cell Biol. 2018 Jun;97(5):359-368. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 4. Eur J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29747876 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the pathogenic potential of the Pentatrichomonas hominis PHGD strain: impact on IPEC-J2 cell growth, adhesion, and gene expression.Parasite. 2024;31:18. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2024014. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Parasite. 2024. PMID: 38530211 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of IRE1α in vascular diseases.J Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Nov 10;18(4):e12056. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.12056. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39691875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Reactive Oxygen Species on the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria during Intracellular Pathogen Infection of Mammalian Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 28;10(6):872. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060872. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34071633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GRP78 determines glioblastoma sensitivity to UBA1 inhibition-induced UPR signaling and cell death.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 23;12(8):733. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04023-w. Cell Death Dis. 2021. Retraction in: Cell Death Dis. 2024 Mar 5;15(3):188. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06574-0. PMID: 34301924 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Case report: Intraabdominal infection of Mycobacterium syngnathidarum in an immunocompetent patient confirmed by whole-genome sequencing.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 5;10:1265594. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1265594. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37869158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattacharyya, A. , Pathak, S. , Basak, C. , Law, S. , Kundu, M. , & Basu, J. (2003). Execution of macrophage apoptosis by Mycobacterium avium through apoptosis signal‐regulating kinase 1/p38 mitogen‐activated protein kinase signaling and caspase 8 activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(29), 26517–26525. 10.1074/jbc.M300852200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choi, J. A. , Lim, Y. J. , Cho, S. N. , Lee, J. H. , Jeong, J. A. , Kim, E. J. , … Song, C. H. (2013). Mycobacterial HBHA induces endoplasmic reticulum stress‐mediated apoptosis through the generation of reactive oxygen species and cytosolic Ca2+ in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Cell Death Dis, 4, e957 10.1038/cddis.2013.489 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

