The Hippo Signaling Pathway in Development and Disease
- PMID: 31386861
- PMCID: PMC6748048
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.06.003
The Hippo Signaling Pathway in Development and Disease
Abstract
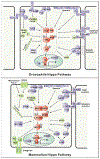
The Hippo signaling pathway regulates diverse physiological processes, and its dysfunction has been implicated in an increasing number of human diseases, including cancer. Here, we provide an updated review of the Hippo pathway; discuss its roles in development, homeostasis, regeneration, and diseases; and highlight outstanding questions for future investigation and opportunities for Hippo-targeted therapies.
Keywords: NF2; TAZ; TEAD; YAP; actomyosin; adherens junction; cancer; cell polarity; cytoskeleton; growth control; hippo signaling; mechanotransduction; merlin; neurofibromatosis; oncogene; regeneration; scalloped; spectrin; tissue homeostasis; tumor suppressor; yorkie.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, Elvassore N, Dupont S, and Piccolo S (2013). A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell 154, 1047–1059. - PubMed
-
- Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E, Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V, et al. (2014). YAP/TAZ incorporation in the beta-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell 158, 157–170. - PubMed
-
- Barolo S, and Posakony JW (2002). Three habits of highly effective signaling pathways: principles of transcriptional control by developmental cell signaling. Genes Dev. 16, 1167–1181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

