Green Extraction of Phenolic Acids from Artemisia argyi Leaves by Tailor-Made Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents
- PMID: 31387251
- PMCID: PMC6695999
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24152842
Green Extraction of Phenolic Acids from Artemisia argyi Leaves by Tailor-Made Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents
Abstract
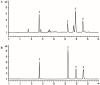
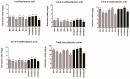
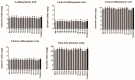
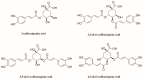
The Artemisia argyi leaf (AL) has been used as a traditional medicine and food supplement in China and other Asian countries for hundreds of years. Phytochemical studies disclosed that AL contains various bioactive constituents. Among bioactive constituents, phenolic acids have been recognized as the main active compounds in AL. To the best of our knowledge, no research has been focused on extraction method for the bioactive phenolic acids from AL. Nowadays, deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are emerging as a new type of green and sustainable solvent for efficient extraction of bioactive compounds from natural products. In the present study, an environmentally friendly extraction method based on DESs was established to extract bioactive phenolic acids from ALs. Diverse tailor-made solvents, including binary and ternary DESs, were explored for simultaneous extraction of four phenolic acids (3-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid, and 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid) from AL. The results indicated that the ternary DES composed of a 2:1:2 molar ratio of choline chloride, malic acid, and urea showed enhanced extraction yields for phenolic acids compared with conventional organic solvents and other DESs. Subsequently, the extraction parameters for the four phenolic acids by selected tailor-made DESs, including liquid-solid ratios, water content (%) in the DESs, and extraction time, were optimized using response surface methodology and the optimal extraction conditions were: extraction time, 23.5 min; liquid-solid ratio, 57.5 mL/g (mL of DES/g dry weight of plant material); water content, 54%. The research indicated that DESs were efficient and sustainable green extraction solvents for extraction of bioactive phenolic acids from natural products. Compared to the conventional organic solvents, the DESs have a great potential as possible alternatives to those organic solvents in health-related areas such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Keywords: Artemisia argyi leaves; deep eutectic solvents; extraction; phenolic acids; response surface methodology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A hybrid RSM-BPNN-GA approach for optimizing ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvents extraction conditions for Mesona chinensis benth. and investigation of the extraction mechanism.J Food Sci. 2024 Sep;89(9):5531-5546. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.17249. Epub 2024 Aug 16. J Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39150703
-
Development and Box-Behnken design optimization of a green extraction method natural deep eutectic solvent-based for phenolic compounds from barley malt rootlets.Electrophoresis. 2022 Oct;43(18-19):1832-1840. doi: 10.1002/elps.202200059. Epub 2022 May 23. Electrophoresis. 2022. PMID: 35512275
-
Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Green Tool for the Extraction of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds from Avocado Peels.Molecules. 2022 Oct 6;27(19):6646. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196646. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235183 Free PMC article.
-
New horizons in the extraction of bioactive compounds using deep eutectic solvents: A review.Anal Chim Acta. 2017 Aug 1;979:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.05.012. Epub 2017 May 26. Anal Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 28599704 Review.
-
The Most Potent Natural Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, and Food Ingredients Isolated from Plants with Deep Eutectic Solvents.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Jul 26;71(29):10877-10900. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01656. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 37433265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Study on the Multitarget Mechanism and Active Compounds of Essential Oil from Artemisia argyi Treating Pressure Injuries Based on Network Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jan 19;2022:1019289. doi: 10.1155/2022/1019289. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35096100 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hydrogen Bond Donor on the Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Natural Matrices Using Deep Eutectic Systems.Molecules. 2021 Apr 17;26(8):2336. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082336. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33920554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artemisia argyi extract alleviates inflammation in a DSS-induced colitis mouse model and enhances immunomodulatory effects in lymphoid tissues.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Mar 11;22(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03536-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35277165 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical Technology in Nutrition Analysis.Molecules. 2020 Mar 17;25(6):1362. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061362. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32192104 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus incrassatulus using natural deep eutectic solvent under microwave assisted by ultrasound.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 24;10(15):e35071. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35071. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39161814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guan X., Ge D., Li S., Huang K., Liu J., Li F. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activities of Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Vant essential oils extracted by simultaneous distillation-extraction, subcritical extraction and hydrodistillation. Molecules. 2019;24:483. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030483. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

