CDDO-Me Selectively Attenuates CA1 Neuronal Death Induced by Status Epilepticus via Facilitating Mitochondrial Fission Independent of LONP1
- PMID: 31387295
- PMCID: PMC6721758
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8080833
CDDO-Me Selectively Attenuates CA1 Neuronal Death Induced by Status Epilepticus via Facilitating Mitochondrial Fission Independent of LONP1
Abstract
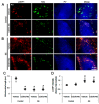
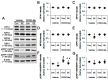
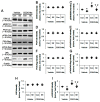
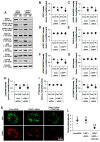
2-Cyano-3,12-dioxo-oleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oic acid methyl ester (CDDO-Me) is a triterpenoid analogue of oleanolic acid that exhibits promising anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective activities. In addition, CDDO-Me affects cellular differentiation and cell cycle arrest, and irreversibly inhibits Lon protease-1 (LONP1). In the present study, we evaluate the effects of CDDO-Me on mitochondrial dynamics and its downstream effectors in order to understand the underlying mechanism of the neuronal death following status epilepticus (SE, a prolonged seizure activity). CDDO-Me increased dynamin-related proteins 1 (DRP1)-serine 616 phosphorylation via activating extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), but not protein kinase A (PKA) or protein phosphatases (PPs). In addition, CDDO-Me facilitated DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fissions, which selectively attenuated SE-induced CA1 neuronal death. Unlike CDDO-Me, LONP1 knockdown led to SE-induced massive degeneration of dentate granule cells, CA1 neurons and hilus interneurons without altering the expression and phosphorylation of DRP1, ERK1/2, JNK and PP2B. LONP1 knockdown could not inhibit SE-induced mitochondrial elongation in CA1 neurons. Co-treatment of CDDO-Me with LONP1 siRNA ameliorated only CA1 neuronal death, concomitant with abrogation of mitochondrial elongation induced by SE. Thus, our findings suggest that CDDO-Me may selectively attenuate SE-induced CA1 neuronal death by rescuing the abnormal mitochondrial machinery, independent of LONP1 activity.
Keywords: 4-HNE; DRP1; ERK1/2; JNK; PKA; TUNEL; hippocampus; mitochondrial dynamics; protein phosphatases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CDDO-Me Attenuates CA1 Neuronal Death by Facilitating RalBP1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and 4-HNE Efflux in the Rat Hippocampus Following Status Epilepticus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 18;11(5):985. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050985. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624848 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC6-Mediated ERK1/2 Activation Increases Dentate Granule Cell Resistance to Status Epilepticus Via Regulating Lon Protease-1 Expression and Mitochondrial Dynamics.Cells. 2019 Nov 1;8(11):1376. doi: 10.3390/cells8111376. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31683954 Free PMC article.
-
LONP1 Regulates Mitochondrial Accumulations of HMGB1 and Caspase-3 in CA1 and PV Neurons Following Status Epilepticus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2275. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052275. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668863 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of CDDO and CDDO-Me, Two Derivatives of Natural Triterpenoids.Molecules. 2019 Nov 13;24(22):4097. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224097. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31766211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bardoxolone methyl (CDDO-Me) as a therapeutic agent: an update on its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Oct 23;8:2075-88. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S68872. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25364233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CDDO-Me Attenuates Astroglial Autophagy via Nrf2-, ERK1/2-SP1- and Src-CK2-PTEN-PI3K/AKT-Mediated Signaling Pathways in the Hippocampus of Chronic Epilepsy Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;10(5):655. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050655. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922531 Free PMC article.
-
CDDO-Me Attenuates CA1 Neuronal Death by Facilitating RalBP1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission and 4-HNE Efflux in the Rat Hippocampus Following Status Epilepticus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 18;11(5):985. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050985. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624848 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria in Health and Diseases.Cells. 2020 May 9;9(5):1177. doi: 10.3390/cells9051177. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32397376 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC6-Mediated ERK1/2 Activation Increases Dentate Granule Cell Resistance to Status Epilepticus Via Regulating Lon Protease-1 Expression and Mitochondrial Dynamics.Cells. 2019 Nov 1;8(11):1376. doi: 10.3390/cells8111376. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31683954 Free PMC article.
-
EGCG Attenuates CA1 Neuronal Death by Regulating GPx1, NF-κB S536 Phosphorylation and Mitochondrial Dynamics in the Rat Hippocampus following Status Epilepticus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 20;12(4):966. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040966. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ribak C.E., Dashtipour K. Neuroplasticity in the damaged dentate gyrus of the epileptic brain. Prog. Brain Res. 2005;136:319–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

