Gracilin A Derivatives Target Early Events in Alzheimer's Disease: in Vitro Effects on Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 31387354
- PMCID: PMC7654966
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00329
Gracilin A Derivatives Target Early Events in Alzheimer's Disease: in Vitro Effects on Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
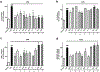
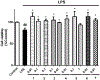
The search for compounds capable of targeting early pathological changes of Alzheimer̀s disease (AD), such as oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, is an important challenge. Gracilin A derivatives were recently synthesized, using a pharmacophore-directed retrosynthesis (PDR) strategy, and found to possess potent neuroprotective effects. In this work, the previously described derivatives 1-7 which demonstrated mitochondrial-mediated, antioxidant effects were chosen for further study. The ability of compounds to modulate the expression of antioxidant genes (CAT, GPx, SODs, and Nrf2) was determined in SH-SY5Y cells, and the simplified derivatives 2 and 3 were found to be the most effective. The anti-neuroinflammatory properties of all derivatives were assessed in BV2 microglial cells activated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Several derivatives decreased the release of cytokines (Il-1β, IL-6, GM-CSF, and TNF-α) and other damaging molecules (ROS, NO) and also regulated the translocation of Nrf2 and NFκB, and reduced p38 activation. These protective effects were confirmed in a trans-well coculture with BV2 and SH-SY5Y cells and several derivatives increased SH-SY5Y survival. This present work demonstrates the neuroprotective properties of gracilin A derivatives, making them promising candidate drugs for AD. Particularly, derivatives 2 and 3 showed the greatest potential as lead compounds for further development.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Gracilin; Nrf2; antioxidant; neuroinflammation; neuroprotection.
Figures


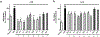


References
-
- Alghazwi M; Kan YQ; Zhang W; Gai WP; Yan XX, Neuroprotective Activities of Marine Natural Products from Marine Sponges. Curr Med Chem 2016, 23 (4), 360–82. - PubMed
-
- Brackovic A; Harvey JE, Synthetic, semisynthetic and natural analogues of peloruside A. Chem Commun (Camb) 2015, 51 (23), 4750–65. - PubMed
-
- Andersen RJ, Sponging off nature for new drug leads. Biochem Pharmacol 2017, 139, 3–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

