Basement membrane collagens and disease mechanisms
- PMID: 31387942
- PMCID: PMC6744580
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20180071
Basement membrane collagens and disease mechanisms
Abstract
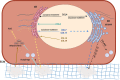
Basement membranes (BMs) are specialised extracellular matrix (ECM) structures and collagens are a key component required for BM function. While collagen IV is the major BM collagen, collagens VI, VII, XV, XVII and XVIII are also present. Mutations in these collagens cause rare multi-systemic diseases but these collagens have also been associated with major common diseases including stroke. Developing treatments for these conditions will require a collective effort to increase our fundamental understanding of the biology of these collagens and the mechanisms by which mutations therein cause disease. Novel insights into pathomolecular disease mechanisms and cellular responses to these mutations has been exploited to develop proof-of-concept treatment strategies in animal models. Combined, these studies have also highlighted the complexity of the disease mechanisms and the need to obtain a more complete understanding of these mechanisms. The identification of pathomolecular mechanisms of collagen mutations shared between different disorders represent an attractive prospect for treatments that may be effective across phenotypically distinct disorders.
Keywords: collagen; extracellular matrix; genetics; model organisms; molecular basis of health and disease; molecular mechanisms.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Mao M., Alavi M.V., Labelle-Dumais C. and Gould D.B. (2015) Type IV collagens and basement membrane diseases: cell biology and pathogenic mechanisms. Curr. Top. Membr. 76, 61–116 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

