Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits invasion and migration of oesophageal cancer cells via up-regulation of microRNA-204
- PMID: 31389660
- PMCID: PMC6787447
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14502
Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits invasion and migration of oesophageal cancer cells via up-regulation of microRNA-204
Abstract
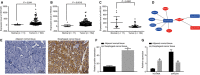
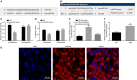
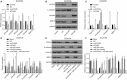
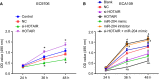
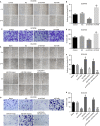
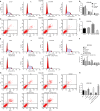
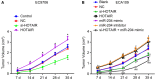
Oesophageal cancer is a progressive tumour with high mortality. However, therapies aimed at treating oesophageal cancer remain relatively limited. Accumulating studies have highlighted long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR), microRNA-204 (miR-204) and homeobox C8 (HOXC8) in the progression of oesophageal cancer. Herein, we tried to demonstrate the function of HOTAIR, miR-204 and HOXC8 in oesophageal cancer and their relationship. Differentially expressed genes involved in oesophageal cancer were identified. The endogenous expression of HOTAIR and miR-204 in oesophageal cancer cell lines was altered to elucidate their effects and to identify the interaction among HOTAIR, miR-204 and HOXC8. We also explored the underlying regulatory mechanisms of HOTAIR and miR-204 with siRNA against HOTAIR, miR-204 mimic or miR-204 inhibitor. Cell proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis were subsequently detected. Xenograft in nude mice was induced to evaluate tumourigenicity. miR-204 was down-regulated, while HOTAIR and HOXC8 were up-regulated in the oesophageal cancer tissues. HOTAIR could competitively bind to miR-204 and miR-204 could further target HOXC8. The oesophageal cancer cells treated with si-HOTAIR or miR-204 mimic exhibited decreased expression levels of HOXC8, Vimentin and MMP-9, but increased E-cadherin level. Silenced HOTAIR or elevated miR-204 inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion, along with stimulated apoptosis of oesophageal cancer cells. In summary, our results show that lncRNA HOTAIR could specifically bind to miR-204 as a competing endogenous RNA and regulate miR-204 and HOXC8. Hence, down-regulation of HOTAIR could inhibit progression of oesophageal cancer, indicating a novel target for oesophageal cancer treatment.
Keywords: HOX transcript antisense RNA; MicroRNA-204; homeobox C8; invasion; long non-coding RNA; migration; oesophageal cancer; proliferation.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
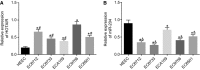
References
-
- Song Y, Li L, Ou Y, et al. Identification of genomic alterations in oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Nature. 2014;509:91‐95. - PubMed
-
- Holmes RS, Vaughan TL. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of esophageal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17:2‐9. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt L, Tirmazy S, Sothi S. Intraluminal high‐dose‐rate brachytherapy for palliation of dysphagia in cancer of the esophagus: initial experience at a single UK center. Dis Esophagus. 2013;26:57‐60. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, Yang T, Xu Z, Cao X. Upregulation of the long non‐coding RNA BANCR correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;82:406‐412. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

