Truncated O-glycans promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties of pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 31389667
- PMCID: PMC6787448
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14572
Truncated O-glycans promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties of pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
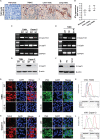
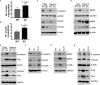
Aberrant expression of Sialyl-Tn (STn) antigen correlates with poor prognosis and reduced patient survival. We demonstrated that expression of Tn and STn in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is due to hypermethylation of Core 1 synthase specific molecular chaperone (COSMC) and enhanced the malignant properties of PDAC cells with an unknown mechanism. To explore the mechanism, we have genetically deleted COSMC in PDAC cells to express truncated O-glycans (SimpleCells, SC) which enhanced cell migration and invasion. Since epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) play a vital role in metastasis, we have analysed the induction of EMT in SC cells. Expressions of the mesenchymal markers were significantly high in SC cells as compared to WT cells. Equally, we found reduced expressions of the epithelial markers in SC cells. Re-expression of COSMC in SC cells reversed the induction of EMT. In addition to this, we also observed an increased cancer stem cell population in SC cells. Furthermore, orthotopic implantation of T3M4 SC cells into athymic nude mice resulted in significantly larger tumours and reduced animal survival. Altogether, these results suggest that aberrant expression of truncated O-glycans in PDAC cells enhances the tumour aggressiveness through the induction of EMT and stemness properties.
Keywords: COSMC; EMT; PDAC; core-1 synthase; stem cells; truncated O-glycans.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359‐E386. - PubMed
-
- Yonezawa S, Tachikawa T, Shin S, Sato E. Sialosyl‐Tn antigen. Its distribution in normal human tissues and expression in adenocarcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992;98:167‐174. - PubMed
-
- Kim GE, Bae HI, Park HU, et al. Aberrant expression of MUC5AC and MUC6 gastric mucins and sialyl Tn antigen in intraepithelial neoplasms of the pancreas. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1052‐1060. - PubMed
-
- Davidson B, Berner A, Nesland JM, et al. Carbohydrate antigen expression in primary tumors, metastatic lesions, and serous effusions from patients diagnosed with epithelial ovarian carcinoma: evidence of up‐regulated Tn and Sialyl Tn antigen expression in effusions. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:1081‐1087. - PubMed
-
- Noda M, Okayama H, Tachibana K, et al. Glycosyltransferase gene expression identifies a poor prognostic colorectal cancer subtype associated with mismatch repair deficiency and incomplete glycan synthesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:4468‐4481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

